Fig. 1.
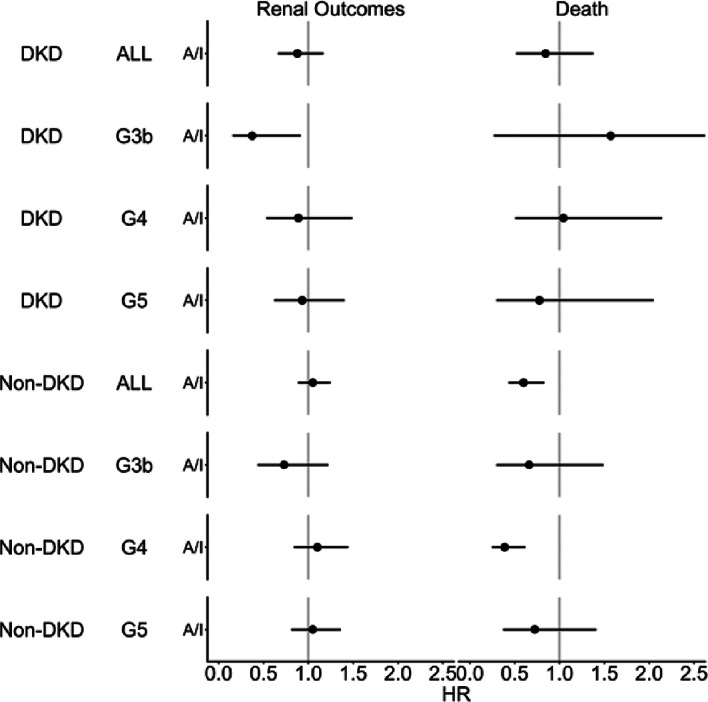
The adjusted hazard ratios of renal outcome and death divided by physical activity (active vs. inactive). DKD diabetic kidney disease, HR hazard ratio, G3b G4, and G5 represents CKD stages. Renal outcome was defined as 40% decline of eGFR from baseline, eGFR < 10 ml/min/1.73m2, or end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis or transplantation, whichever occurred first. Models were adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, body mass index, eGFR, level of proteinuria, serum albumin, hemoglobin, diabetes, comorbidity score, cognitive heart failure, and lung disease. The comorbidity score was calculated per patient as the number of comorbidities out of the following 10: coronary heart disease, hypertension, other cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, recurrent cellulitis/gangrene, neurologic disease, psychiatric disorder, gastrointestinal bleeding, and cancer.
