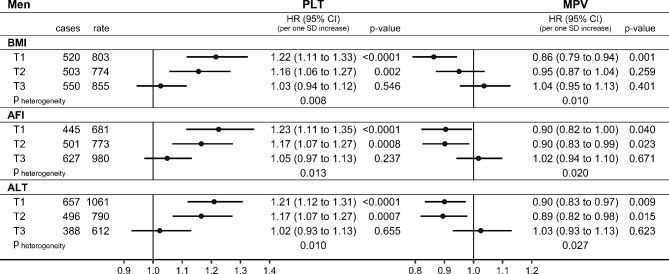
Fig. 2.
Associations of platelet parameters with lung cancer risk (men): groups by BMI, AFI, ALT tertiles. AFI: allometric fat-mass index (cut-offs: 10.293; 13.703); ALT: alanine aminotransferase (cut-offs: 20.25; 28.65 IU/L); BMI: body mass index (cut-offs: 25.806; 28.982 kg/m2); CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; MPV: mean platelet volume; PLT: platelet count; SD: standard deviation; T1-T3: sex-specific tertiles; cases: number of lung cancer cases; rate: incidence rate per 1*106 person years; p-value: p-value from Wald test for the individual term; pheterogeneity: p-value comparing the association with lung cancer risk between the highest sex-specific tertile group and the combined group of the middle and lowest tertile with the augmentation method of Lunn and McNeil23. Cox proportional hazards models in groups according to tertiles of either BMI, AFI, or ALT in men, including as exposure either PLT or MPV (sex-specific z-scores, value minus mean divided by standard deviation after log-transformation), stratified by age at recruitment, region, and smoking status and intensity, and adjusted for height, recent weight gain, alcohol consumption, physical activity, Townsend deprivation index, family history of lung cancer, time of blood collection, fasting time, diabetes, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, antihypertensive drugs, antiaggregant/anticoagulants, and paracetamol.