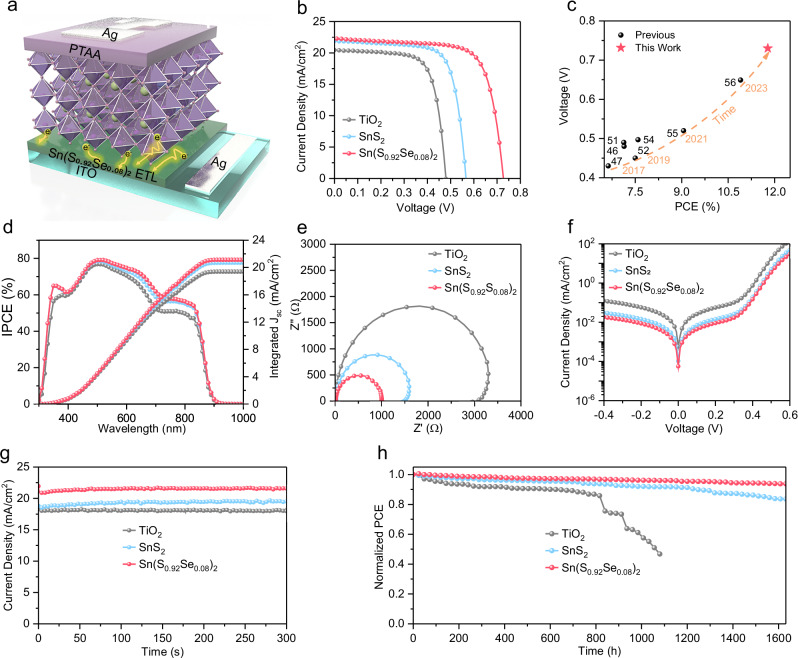
Fig. 4. Photovoltaic performance of TPSCs with metal chalcogenide ETLs.
a Schematic diagram of nip-type TPSCs with the structure of FTO/ETL/Sn-based perovskite/PTAA/Ag, utilizing TiO2, SnS2, and Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 films as ETLs. b J–V curves of nip-type TPSCs with TiO2, SnS2 and Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 ETLs, respectively. c A comparison of PCE between this work and other reported PCEs (over 6.5%) of nip-type TPSCs. The impressive PCE of the nip-type TPSC with the Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 film significantly surpasses those of previously reported nip-type TPSCs with TiO2 films. d EQE spectra and integrated Jsc values of the nip-type TPSCs with TiO2, SnS2 and Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 ETLs, respectively. e Nyquist plots. f dark J–V curves, and (g) stabilized power output of nip-type TPSCs with TiO2, SnS2 and Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 ETLs respectively. These result indicate that the nip-type TPSC with the Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 ETL showcases the reduced charge transfer resistance, fastest electron transport, and lowest defect density among the three types ETLs. h Normalized PCE of unencapsulated nip-type TPSCs with TiO2, SnS2 and Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2 ETLs for over 1600 h in an N2 glovebox. These findings collectively support the potential of metal chalcogenide ETLs, particularly Sn(S0.92Se0.08)2, for advancing the performance and stability of nip-type TPSCs.