Figure 3.
SKIV2L helicase activity is dispensable for the suppression of telomere fragility
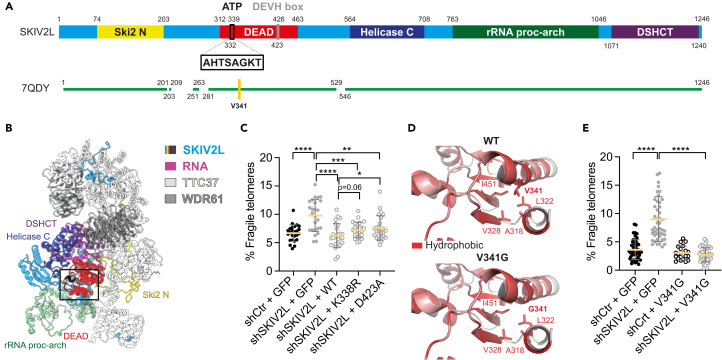
(A) Schematic diagram to illustrate the domain organization and features of human SKIV2L. The structurally resolved (via cryo-EM) regions of the SKIV2L subunit extracted from the RNA-bound human SKI complex in the closed state (PDB: 7QDY) is represented by a green colored bar. The SKIV2L subunit harbors the following domains: Ski2 N-terminal (Ski2 N) domain, DEAD/DEAH box helicase (DEAH) domain, ATP binding (ATP) domain, Helicase C-terminal (Helicase C) domain, rRNA-processing arch (rRNA proc-arch) domain and DOB1/SK12/helY-like DEAD box helicases C-terminal (DSHCT) domain. The SKIV2L-V341 residue is highlighted in yellow.
(B) Overview of the structure of the RNA-bound human SKI complex in the closed state, featuring: the helicase SKIV2L, tetratricopeptide repeat protein 37 (TTC37) and WD repeat-containing protein 61 (WDR61).
(C) Telomeric FISH analysis: % of telomere fragility in shCtr and shSKIV2L HEK293 cells expressing GFP or SKIV2L (WT), SKIV2L-K338R, SKIV2L-D423A (means ± SD, n > 20 metaphases, 2 independent experiments). t test ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, significance is not shown for comparisons with p > 0.06.
(D) Comparison of the structure of the wild-type (WT) SKIV2L DEAD domain and a mutant structure, generated using Missense3D, featuring a valine to glycine 341 mutant. In the WT structure, V341 forms hydrophobic contacts with: A318, L322, V328 and I451. The hydrophobic surface shown is colored according to the Eisenberg hydrophobicity scale.
(E) Telomeric FISH analysis: % of telomere fragility in shCtr and shSKIV2L HEK293 cells expressing GFP or SKIV2L-V341G (means ± SD, n > 20 metaphases, 2 independent experiments). t test ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. See also Figure S3.