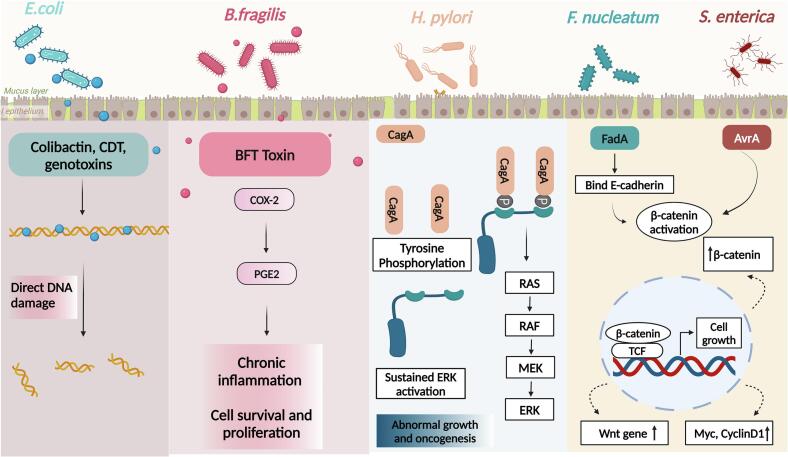
Fig. 4.
Microbial inducers of carcinogenesis. Genotoxin-producing bacteria E. coli and B. fragilis drive carcinogenesis by inducing direct DNA damage and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 mediated signaling, respectively. H. pylori produces cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) bacterial protein which bind to the phosphorylated Src homology 2 (SH2) domain leading to an increase in ERK levels driving oncogenesis. The virulence factors produced by F. nucleatum and S.enterica induce activation of β-catenin which upon translocation to the nucleus results in overexpression of a variety of genes involved in cell proliferation, such as Myc, CycinD1, Wnt etc.