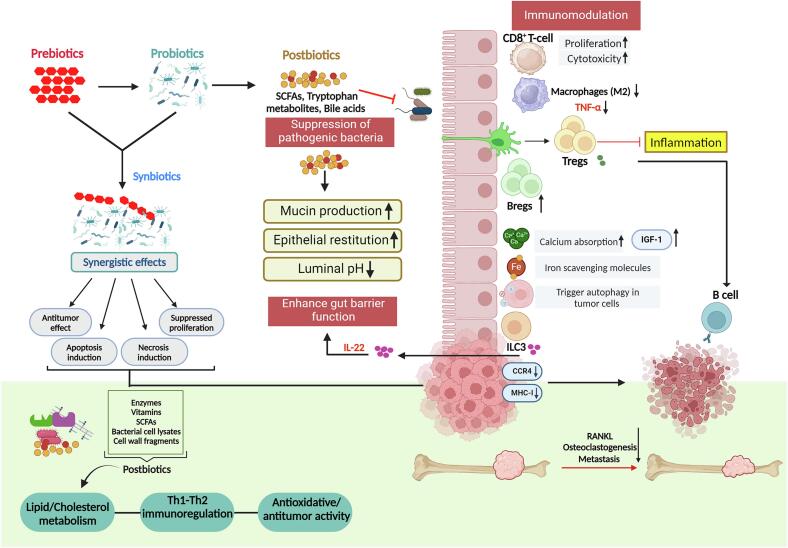
Fig. 6.
Modulation of gut microbiota (GM) for therapeutic purposes. Prebiotics and probiotics, including the gut-associated short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) exert anti-cancer effects by preventing the epithelial breach by pathogenic bacteria. This is mediated by activation of the immune machinery to enhance the integrity of gut barrier function by release of interleukin (IL)-22 from innate lymphoid cell (ILC)3s. Activation of dendritic cells (DC)s stimulate Th17 cells to produce IL-17A which has an anti-tumor effect. SCFAs also play a crucial role in maintaining luminal pH and mucin secretions, keeping up with the epithelial integrity. Synbiotics and postbiotics, which include bacterial cell lysates, enzymes, vitamins, SCFAs, and cell wall fragments, also have anti-cancer effects resulting in tumor regression.