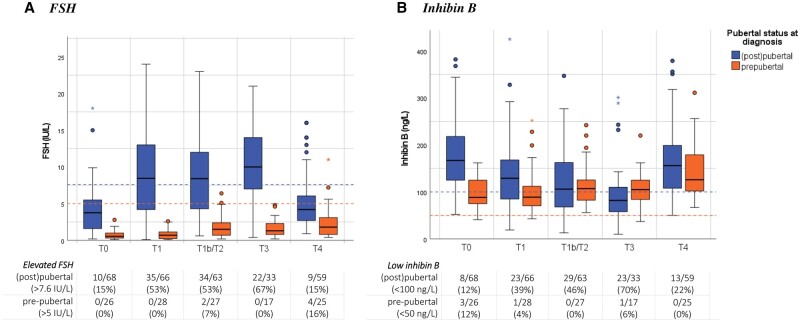
Figure 3.
Serum FSH and inhibin B during treatment for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma up to 2 years follow-up in pre- and (post)pubertal boys. (A) FSH, B inhibin. (B) Boxplots depicting the distribution of uncorrected serum FSH or inhibin B from diagnosis up to 2 years post-diagnosis, including the median (centerline), interquartile range (end of the box), and range (end of the whiskers). Separate dots are outliers. Patients who were pre-pubertal at time of diagnosis are shown in orange, and boys who were (post)pubertal at diagnosis (definition testicular volume ≥4 ml or in case of missing Tanner-G ≥2) are shown in blue. The dashed lines in blue highlight applied cut-off scores to define normal (≤7.6 IU/l) or high FSH (>7.6 IU/l), respectively normal (≥100 ng/l) or low inhibin B (<100 ng/l) in (post)pubertal boys. The dashed lines in orange highlight applied cut-off scores to define normal (≤5 IU/l) or high FSH (>5 IU/l), respectively normal- (≥50 ng/l) or low inhibin B (<50 ng/l) in pre-pubertal boys. FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; N, number. Timing sampling: T0, at diagnosis; T1, after 2× OEPA; T1b, after 1× COPDAC; T2, after 2×(DE)COPDAC; T3, after 4×(DE)COPDAC; T4, 2 years post-diagnosis.