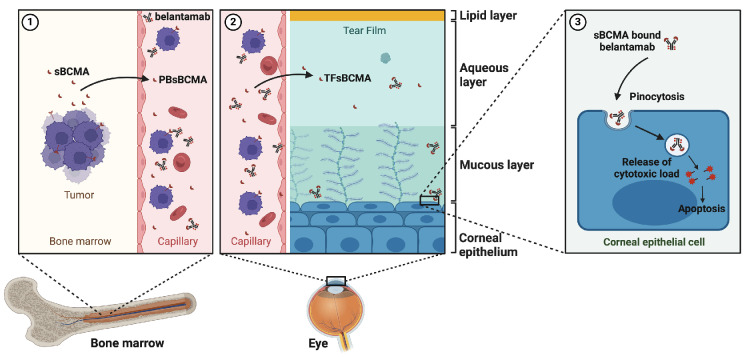
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism of belantamab-induced keratopathy. (1) Upon high tumor burden or sudden tumor lysis, soluble B-cell maturation antigen (sBCMA) is shed from the surface of bone marrow-residing multiple myeloma (MM) cells to circulate into the bloodstream. (2) Serum sBCMA crosses the endothelial barrier at the corneal limbus of the eye and enters the lacrimal fluid; the amount of sBCMA in the tear fluid may serve as proxy for tumor load in the body. (3) In its bound form to sBCMA, belantamab is carried to the lacrimal fluid and absorbed by corneal epithelial cells via fluid endocytosis (pinocytosis). Inside the cell, belantamab is subsequently released via hydroxylation leading to apoptosis of the corneal epithelium. PB: peripheral blood; TF: tear film. (Created with Biorender.com).