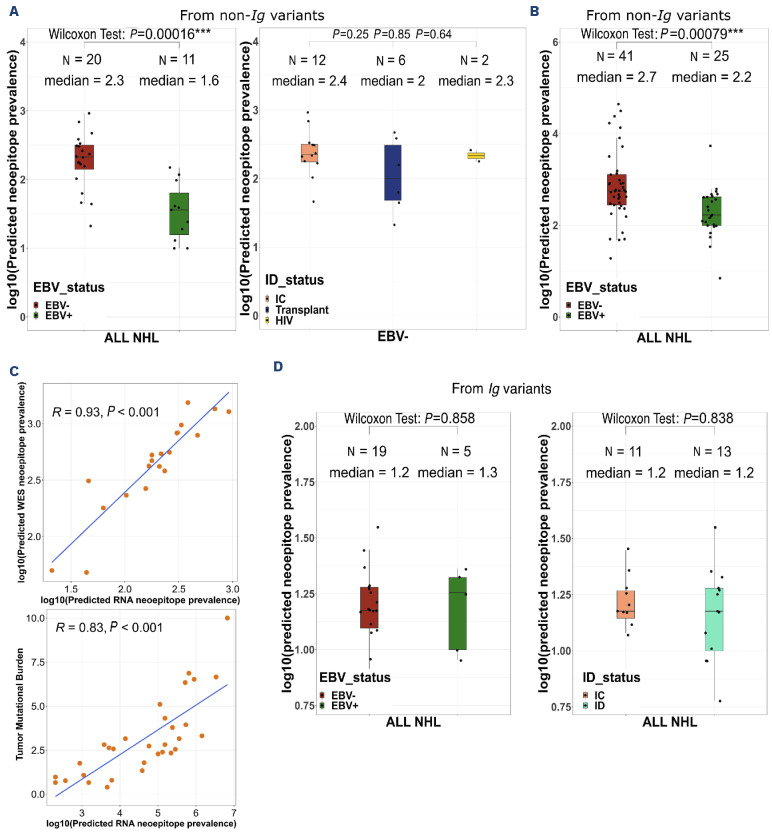
Figure 3.
The number of neoepitopes is lower in Epstein-Barr virus-positive non-Hodgkin lymphoma than in Epstein-Barr virus-negative cases. (A) Number of predicted neoepitopes (log10) from the non-Ig variants within the 31 RNA samples, according to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status on the left and immune status (in EBV– non-Hodgkin lymphoma) on the right. Wilcoxon test. (B) Number of predicted neoepitopes (log10) from the non-Ig variants within the 66 whole-exome sequencing samples (2 samples were excluded because of absence of germline assessment) according to EBV status. Wilcoxon test. (C) Correlation study between the number of predicted neoepitopes from the RNA and the whole-exome sequencing data (top) and between the number of predicted neoepitopes from the RNA data and the tumor mutational burden (bottom). Spearman correlation. (D) Number of predicted neoepitopes (log10) from Ig variants within the 24 RNA samples (7 samples were excluded because of dominant IgH clone <15%). Wilcoxon test. NHL: non-Hodgkin lymphoma; ID: immunodeficient; IC: immunocompetent; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; WES: whole-exome sequencing.