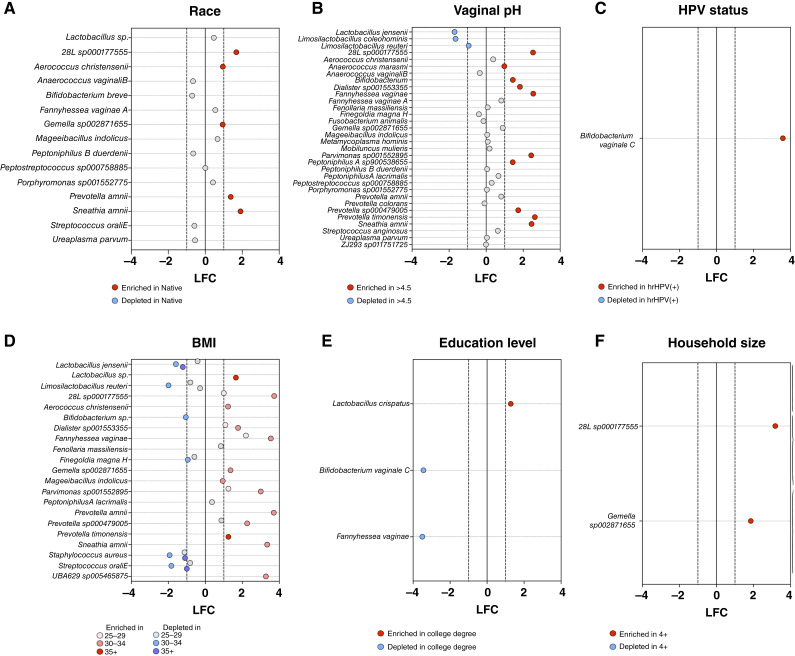
Figure 3.
Microbial features associated with sociodemographic factors, vaginal pH, and HPV status. Differentially abundant taxa between the groups based on A, race, B, vaginal pH, C, HPV status, D, BMI, E, education level, and F, household size were identified at the species level using ANCOM-BC. P values were corrected for multiple comparisons using the FDR method; taxa with q < 0.05 are depicted. Red and blue dots indicate taxa with LFC > 1 and LFC < −1, respectively. Numerous dysbiotic vaginal species are enriched in participants with abnormal vaginal pH, lower education level, who live in larger households, identify themselves as Native American, have higher BMI, and are hrHPV-positive, whereas Lactobacillus and Limosilactobacillus species were enriched in women with normal pH, higher education level and lower BMI.