FIGURE 5.
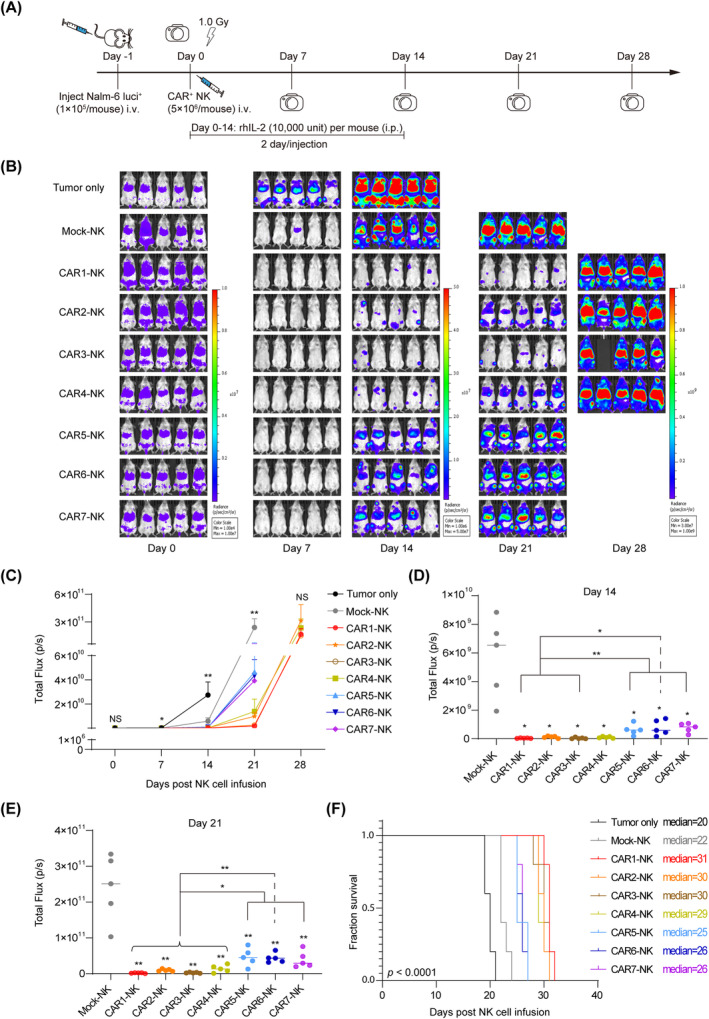
Inhibition of human B leukaemia development in xenograft models by seven types of CD19 CAR‐NK cells. (A) Schematic diagram of in vivo studies with luciferase‐expressing (luci+) Nalm‐6 cells (1 × 105 cells/mouse, i.v.) in mouse xenograft models. The equivalent of 5 million CD19 CAR‐NK cells were infused into each animal. rhIL‐2 (10,000 IU/mouse, i.p.) was administered every 2 days until Day 14 post‐NK infusion. (B) Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of xenograft models (Tumour only, Tumour + Mock‐NK, and Tumour + seven CD19 CAR‐NK, n = 5 animals per group). (C) Statistics of the total flux (p/s) of each group after NK cell infusion. Statistics: Kruskal–Wallis tests, one‐way ANOVA, and two‐tailed Student's t test. On Day 7, Tumour only versus Mock‐NK, p < 0.05. On Day 14, Tumour only versus Mock‐NK, p < 0.01. On Day 21, Mock‐NK versus seven CAR‐NK, p < 0.01. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, NS, not significant. (D, E) BLI quantification of tumour burden on Day 14 and 21, displayed as mean ± SD. Mock‐NK versus each CAR‐NK group; statistics: one‐way ANOVA and two‐tailed Student's t test. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. (F) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of the xenograft models. Comparisons between groups provided with specified p values. Tumour only versus Mock‐NK, p < 0.01. Mock‐NK versus seven CAR‐NK, p < 0.01; statistics: two‐tailed log‐rank test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; NK, natural killer.
