Abstract
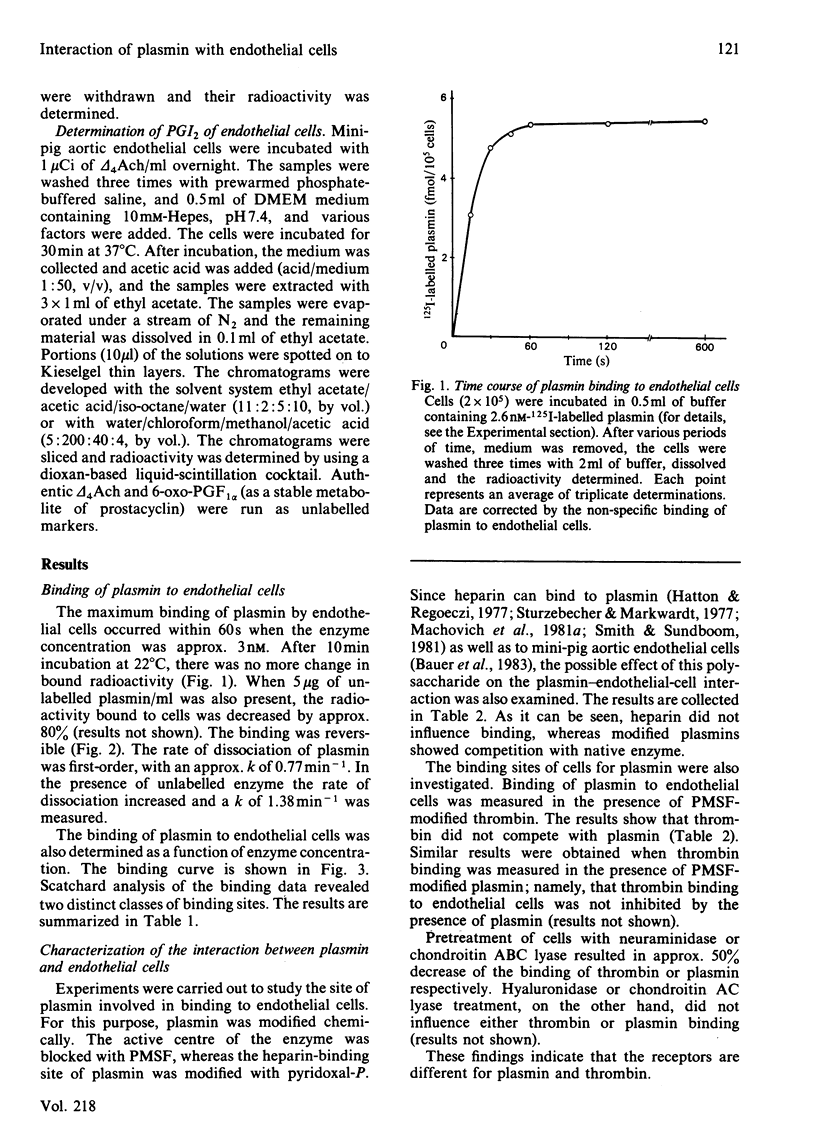
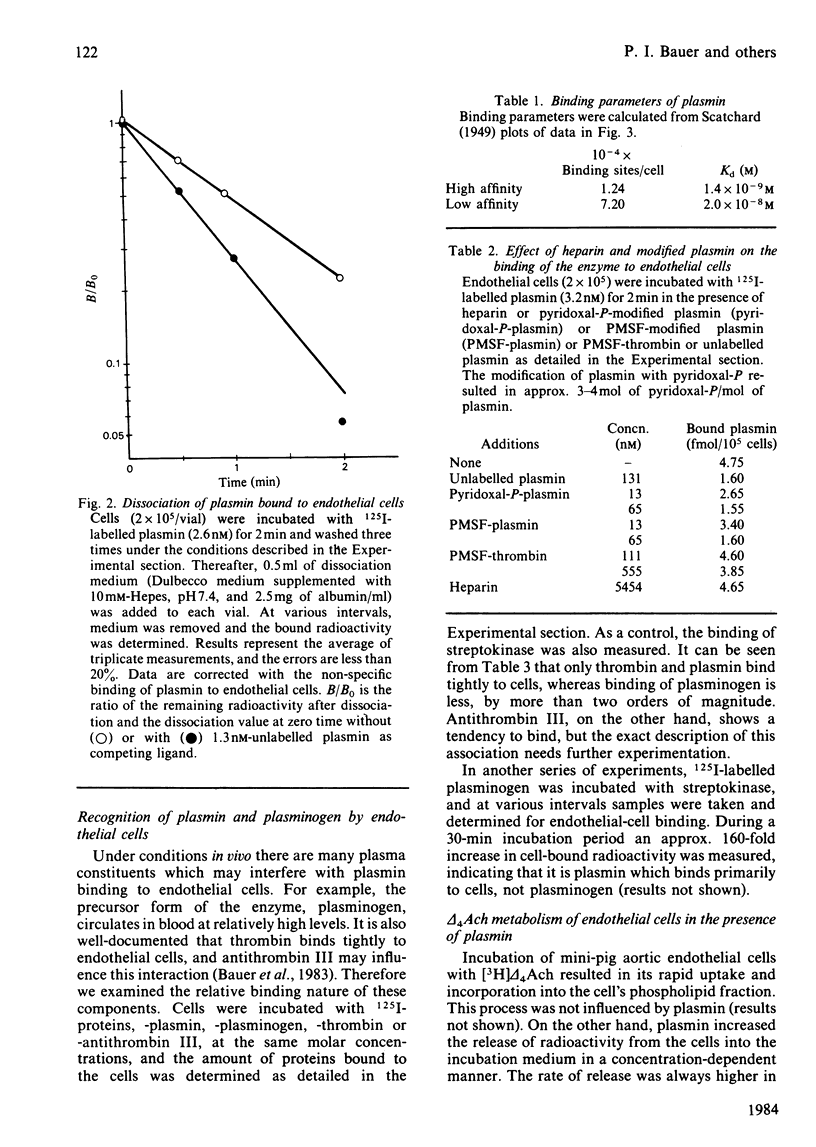
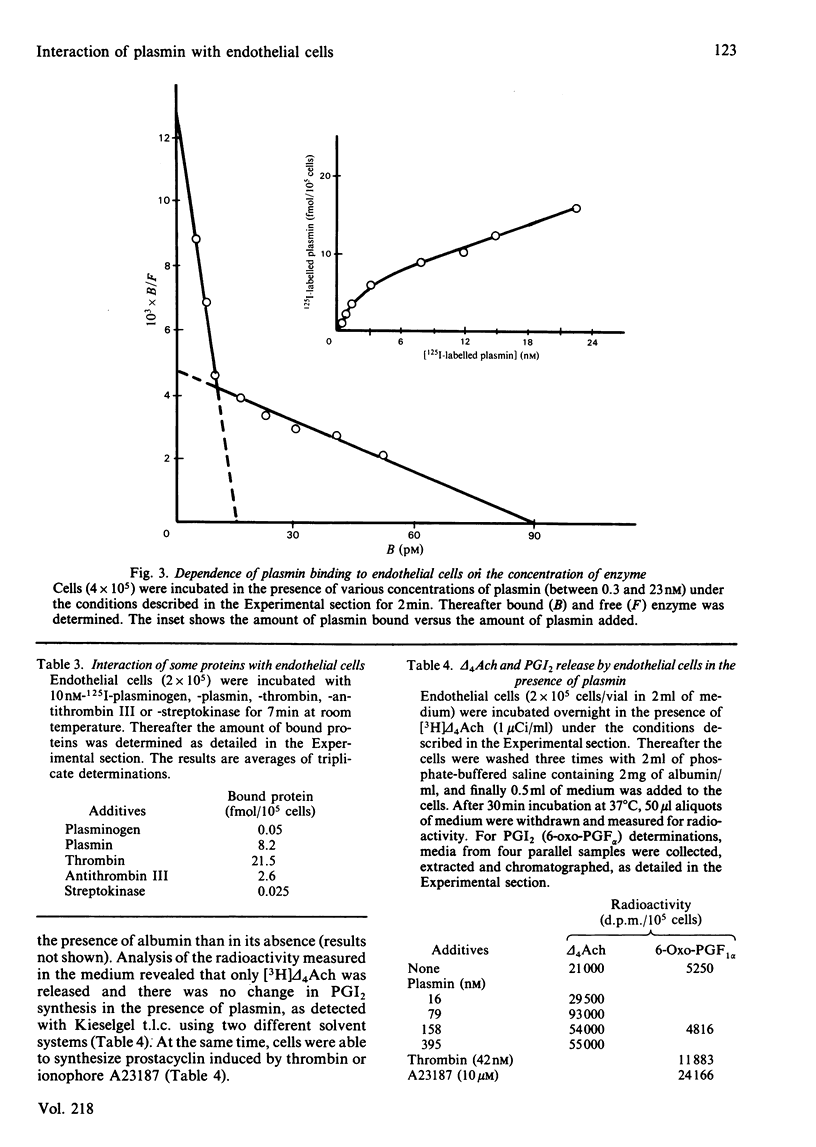
Interaction of human plasmin with a monolayer culture of mini-pig aortic endothelial cells was studied by using the 125I-labelled enzyme. The binding of plasmin was time- and concentration-dependent. Equilibrium between bound and free enzyme was obtained within 90s, and Scatchard analysis indicated a high- and a low-affinity population of binding sites of approx. 1.24 X 10(4) sites/cell having a Kd of 1.4 X 10(-9) M and 7.2 X 10(4) sites/cell with a Kd of 2 X 10(-8) M respectively. Plasmin, bound to cell, was spontaneously released within 2 min, suggesting a rapid equilibrium. Chemical modification of the enzyme with phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride or pyridoxal 5'-phosphate revealed that neither the active centre nor the heparin-binding site of plasmin was involved in the interaction with the endothelial cell. In terms of endothelial-cell receptors, the binding sites of cells for plasmin and thrombin were different: the two enzymes did not compete with each other, and the pretreatment of cells with neuraminidase or chondroitin ABC lyase resulted in a 50% decrease of thrombin or plasmin binding respectively. Arachidonic acid incorporated into phospholipids of the cell was released by plasmin, but a change in the rate of prostacyclin formation was not measurable. The interaction of plasmin with endothelial cells seems to be specific in the fibrinolytic system, since plasminogen did not bind to these cells under similar conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnhart M. I., Baechler C. A. Endothelial cell physiology, perturbations and responses. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1978 Fall;5(2):50–86. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. T., Machovich R., Arányi P., Büki K. G., Csonka E., Horváth I. Mechanism of thrombin binding to endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka E., Szemenyei K., Miskulin M., Robert A. M. Morphological examination of aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells grown in vitro on collagen membranes. Artery. 1980;8(3):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. The inactivation of thrombin and plasmin by antithrombin III in the presence of sepharose-heparin. Thromb Res. 1977 May;10(5):645–660. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes L. W., Goguen C. A., Ching S. F., Slakey L. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: accumulation in medium from cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1147–1153. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope W., Martin T. J., Chesterman C. N., Morgan F. J. Human beta-thromboglobulin inhibits PGI2 production and binds to a specific site in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):210–212. doi: 10.1038/282210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerënyi T., Koch A. S., Jellinek H., Csonka E. In vitro cultivation and identification of aortic endothelium from miniature pig. Paroi Arterielle. 1975 Sep;3(1):31–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. Nonequilibrium aspects. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10279–10283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Evidence that the effects of thrombin on arachidonate metabolism in cultured human endothelial cells are not mediated by a high affinity receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8031–8034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. E. Synthesis of a fibrinolytic activator and inhibitor by endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effect of thrombin on the fibrinolytic activity of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI109457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machovich R., Bauer P. I., Arányi P., Kecskés E., Büki K. G., Horváth I. Kinetic analysis of the heparin-enhanced plasmin--antithrombin III reaction. Apparent catalytic role of heparin. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):521–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1990521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. R., Dreyer B. E., Stemerman M. B., Pitlick F. A. Tissue-factor coagulant activity of cultured human endothelial and smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):387–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMMERT L. F., COHEN P. P. Partial purification and properties of a proteolytic enzyme of human serum. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):431–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., Sundboom J. L. Heparin and protease inhibition. I. Heparin complexes with thrombin, plasmin, and trypsin. Thromb Res. 1981 Apr 1;22(1-2):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smokovitis A. A new hypothesis: possible mechanisms in the involvement of the increased plasminogen activator activity in branching regions of the aorta in the initiation of atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzebecher J., Markwardt F. Role of heparin in the inactivation of thrombin, factor Xa, and plasmin by antithrombin III. Thromb Res. 1977 Dec;11(6):835–846. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickerhauser M., Williams C., Mercer J. Development of large scale fractionation methods. VII. Preparation of antithrombin III concentrate. Vox Sang. 1979;36(5):281–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1979.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Loskutoff D. J., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H., Edgington T. S. Activation of rabbit Hageman factor by homogenates of cultured rabbit endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):197–206. doi: 10.1172/JCI109651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


