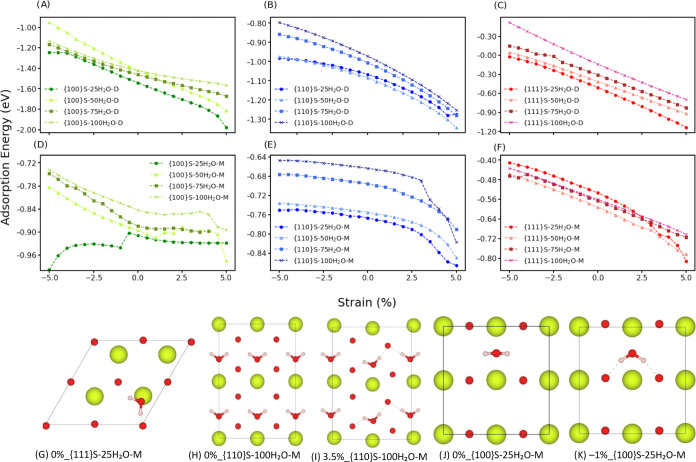
Figure 2.
Adsorption energy of water on CeO2 surfaces as a function of strain and water coverages (25–100%): dissociative water on the (A) {100}, (B) {110}, and (C) {111} surfaces, and molecular water on the (D) {100}, (E) {110}, and (F) {111} surfaces. The structure of adsorbed molecular water on (G) {111}, (H, I) {110}, and (J, K) {100} unstrained and strained surfaces.