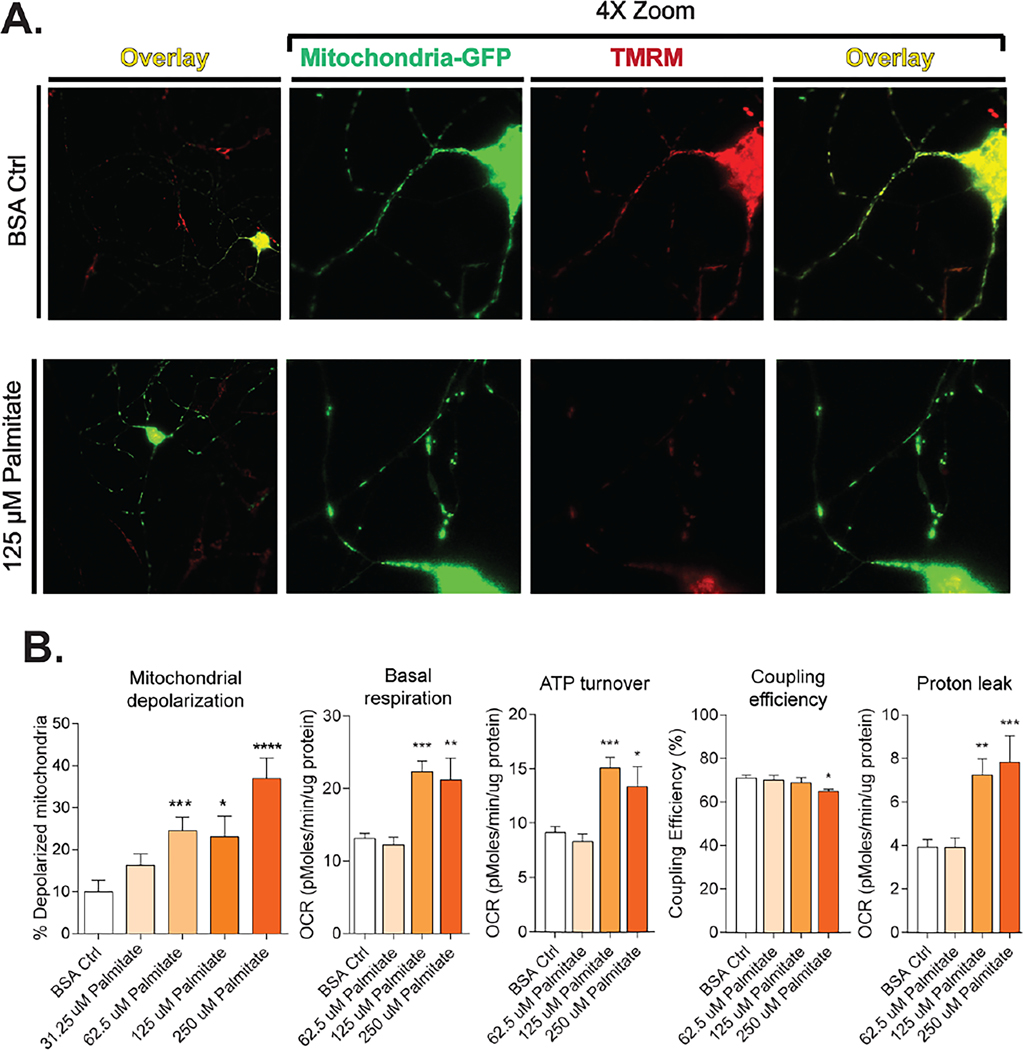
Fig. 3.
Dyslipidemia decreases mitochondrial function in DRG neurons. (A) LCSFA palmitate induces a loss of MMP through mitochondrial depolarization. Mitochondria labeled with mito-GFP are stained with MMP-dependent stain TMRM. Axonal mitochondria maintain MMP in the bovine serum albumin vehicle control and appear yellow in an overlay of both signals. Palmitate-treated cells exhibit a loss in TMRM staining due to mitochondrial depolarization. (B) Palmitate impairs mitochondrial bioenergetics through mitochondrial depolarization by increasing basal respiration and ATP turn over which leads to a decrease in coupling efficiency and increased proton leak from the electron transport chain. Bioenergetics bar graphs included with permission from Rumora, A.E., Lentz, S.I., Hinder, L.M., Jackson, S.W., Valesano, A., Levinson, G.E., and Feldman, E.L. (2018). Dyslipidemia impairs mitochondrial trafficking and function in sensory neurons. Faseb j 32, 195–207. Mitochondrial depolarization figures adapted with permission from Rumora, A.E., LoGrasso, G., Haidar, J.A., Dolkowski, J.J., Lentz, S.I., and Feldman, E.L. (2019). Chain length of saturated fatty acids regulates mitochondrial trafficking and function in sensory neurons. J Lipid Res 60, 58–70.