FIGURE 9.
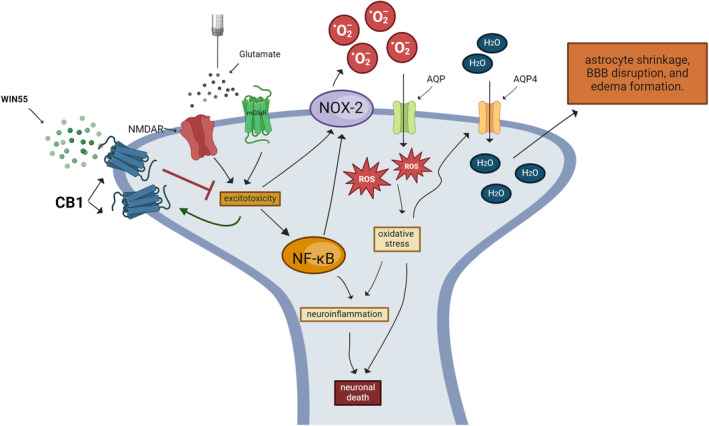
Molecular mechanism implicated in the neuroprotective action of WIN55 in the excitotoxicity induced by glutamate. WIN55 reduces neuronal death, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and NOX‐2 activity. The action of the CB1 receptor must be located upstream of all these processes. Glutamate induces the expression of the CB1R that could reinforce the neuroprotective action of WIN55. In astrocytes, the decline in ROS production reduces AQP4 levels and attenuates BBB disruption as well as edema formation.
