Fig. 1. Finite-element simulations of a quantum dot coupled to a mechanical resonator.
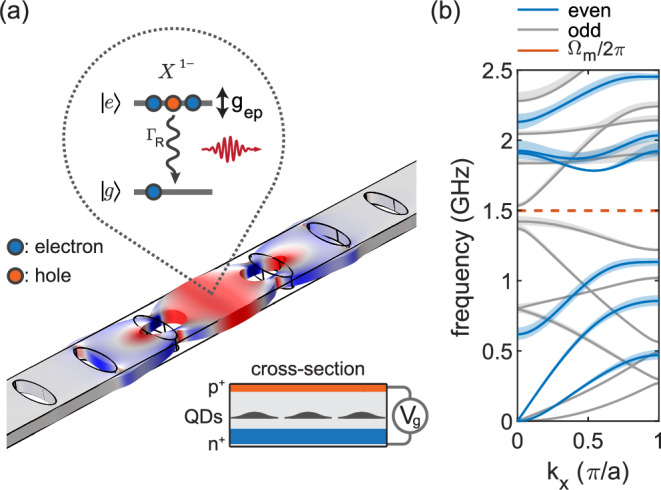
a Phononic-crystal resonator hosting a semiconductor diode-structure for quantum dot (QD) charge control (see cross-section). The QD emits single photons and its excited state is dispersively coupled to the mechanical motion via a deformation potential (example given for the negative trion X1−). The resonator consists of a well-isolated mechanical mode at Ωm/2π ≈ 1.5 GHz tightly confined by the surrounding phononic shield. b Band diagram of the phononic shield. The width of the bandgap is 0.65 GHz and 0.11 GHz for even and odd modes in terms of the z-symmetry, respectively. Shaded areas represent band broadening upon varying the air-hole parameters by ±20 nm.
