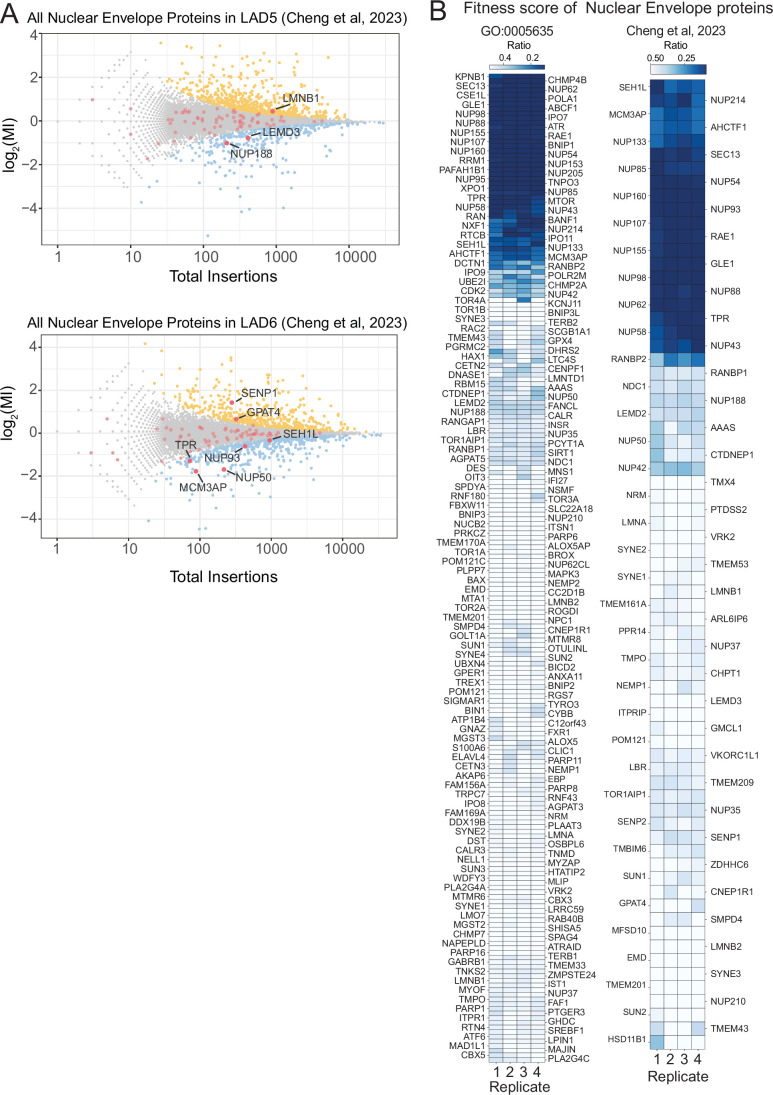
Figure EV2. Nuclear Lamina genes in the screen and their essentiality in HAP1 cells.
(A) Biochemically identified NE proteins (Cheng et al, 2019) (red dots) highlighted in the screen fishtail plots for LAD5 (top) and LAD6 (bottom). The majority of these NE proteins are not significant hits in the screens. Names of the handful of significant screen hits are indicated in black. (B) Essentiality scores of proteins in GO category GO:0005635 (left panel) and of proteins biochemically identified as NE proteins (Cheng et al, 2019), (right panel). Heatmaps show the ratio of sense insertions to the total insertions in wild-type HAP1 cells across 4 independent replicates under untreated conditions. Data are from (Blomen et al, 2015). The scores represent the ratio of disruptive insertions (sense) to the total insertions (sense “disruptive” + antisense “non-disruptive”) within the intronic regions of each gene. Genes crucial for cell viability will have fewer disruptive insertions as these cells are depleted, whereas cells with non-disruptive (antisense) insertions survive. As disruptive and non-disruptive integrations occur at similar frequencies, the ratio of insertions in the surviving population indicates whether a gene is important for cell fitness (Blomen et al, 2015). The lower the ratio (blue shading), the more important the gene is for HAP1 cell fitness. Results from 4 different biological replicates are shown separately.