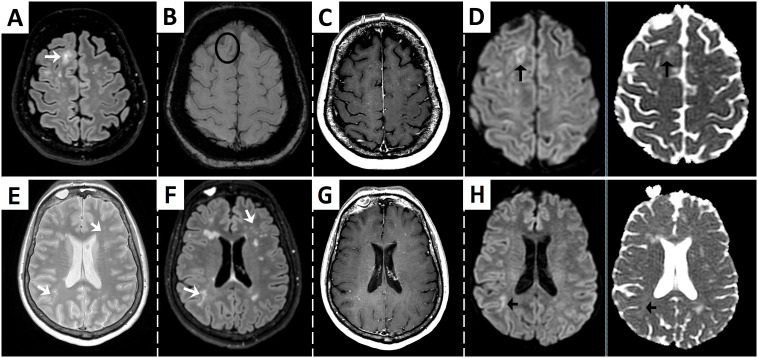
Figure 1.
Brain MRI at presentation showing findings suggestive of multifocal progressive leukoencephalopathy and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence shows an ill-defined subcortical and juxtacortical hyperintense lesion [arrow in (A)], with a paramagnetic rim adjacent to the cortex in susceptibility-weighed imaging suggestive of iron deposition [circle in (B)]. T1-weighted post-gadolinium sequence reveals punctate hyperintensities that suggest enhancement or perivascular spaces (C). Diffusion-weighed (DWI) imaging shows a hypointense core surrounded by restriction at the periphery [left arrow in (D)]. ADC map demonstrates variable low ADC values of similar intensity to surrounding normal white matter [right arrow in (D)]. Other ill-defined and punctate lesions can be seen in T2 and FLAIR images (arrows in (E, F), respectively), with punctate enhancement [T1-weighted post-gadolinum image in (G)] and restricted diffusion of a right subcortical lesion [arrows in (H)].