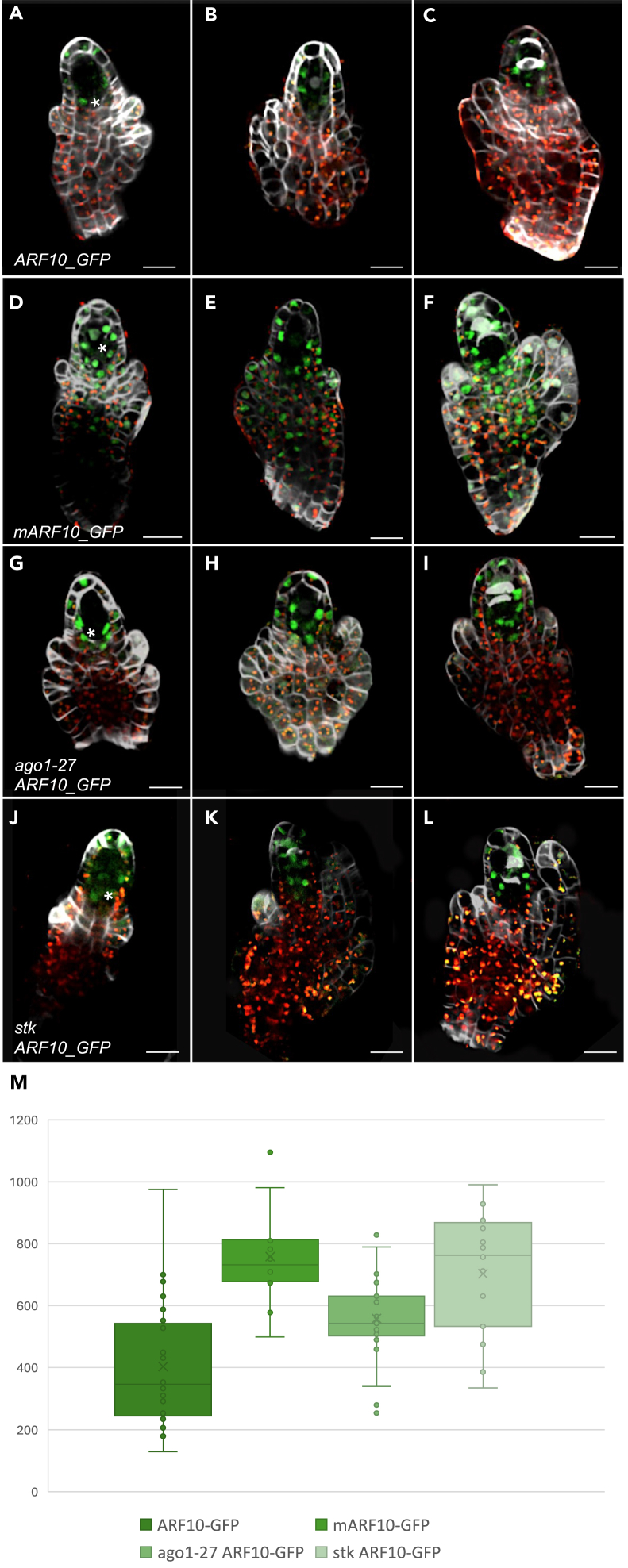
Figure 5.
ARF10 expression patterns in different genetic contexts
(A and B) In wild type context, ARF10_GFP expression at pre-meiosis is detected in a few cells surrounding the MMC.
(C) in the post-meiotic ovule, ARF10_GFP expression is maintained in few L2 cells surrounding the meiocytes.
(D and E) mARF10_GFP expression pattern at pre-meiosis, a strong GFP signal is detected in all ovule cells, including the MMC.
(F) mARF10_GFP expression at post-meiosis, the GFP signal is detected in all ovule cells, including the funiculus and chalaza.
(G–I) ARF10_GFP protein accumulation in ago1-27 nucellar cells at three successive developmental stages, from MMC differentiation to meiosis. The expression is observed in the same domain as for the wild type context, but the signal is stronger (see quantification).
(J–L) ARF10_GFP protein accumulation in stk nucellar cells at three successive developmental stages, from MMC differentiation to meiosis. The expression is observed in the same domain as for the wild type context, but an increased signal is detected within the MMC. The signal is stronger (see quantification).
(M) mean GFP intensity detected in the nucellus for the different genotypes: mARF10, ago1 and stk backgrounds showed significantly higher signal levels with respect to wild type ones. Data are represented in a dot plot as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.01) showed significant differences in GFP expression levels between WT and mARF10, ago1-27 ARF10_GFP, and stk ARF10_GFP. Scale bars: 20 μm. Cell walls were stained using Renaissance. Green signal corresponds to GFP.