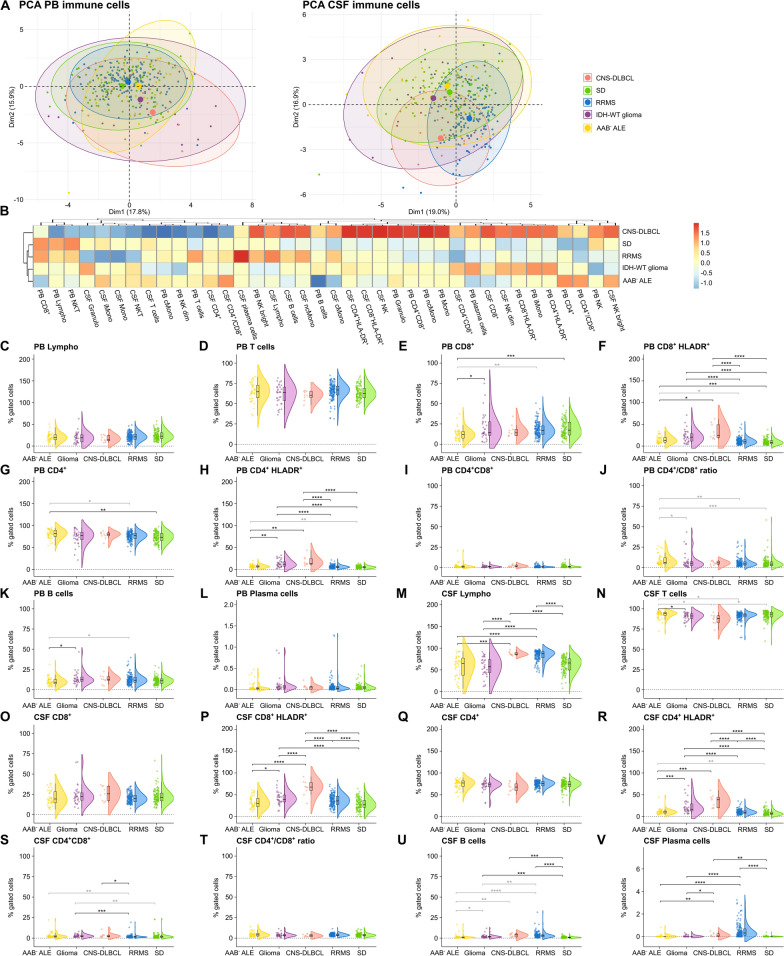
Fig. 2.
Antibody-negative ALE features similarities in adaptive immunity with IDH-wildtype glioma, and CNS-DLBCL. A PCA including either PB mFC or CSF mFC parameters (% of gated cells) of AAB− ALE, RRMS, IDH-wildtype glioma, CNS-DLBCL, and SD patients. Every patient is displayed as a colored symbol. B Heatmap analysis of PB and CSF mFC parameters (% of gated cells) from AAB− ALE, RRMS, IDH-wildtype glioma, CNS-DLBCL, and SD patients: the median of each parameter was calculated, scaled, centered, and clustered hierarchically; C–V Violin plots with overlaying box plots depicting the PB and CSF mFC parameters of AAB− ALE, RRMS, IDH-wildtype glioma, CNS-DLBCL, and SD patients. The whiskers extend from the hinge to the largest and smallest values, respectively, but no further than 1.5 * IQR from the hinge. P-values were calculated by ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD if normality could be assumed based on Shapiro–Wilk test, otherwise Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn post hoc test (p-adjustment method: Benjamini–Hochberg) was used. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. AAB− ALE Antibody-negative autoimmune limbic encephalitis, CD4+/CD8+ CD4+/CD8+ ratio, CNS Central nervous system, CSF cerebrospinal fluid, CNS-DLBCL diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the central nervous system, IDH isocitrate dehydrogenase, Lympho lymphocytes; mFC multidimensional flow cytometry, PB peripheral blood, PCA principal component analysis, RRMS relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, SD somatic symptom disorder, WT wildtype