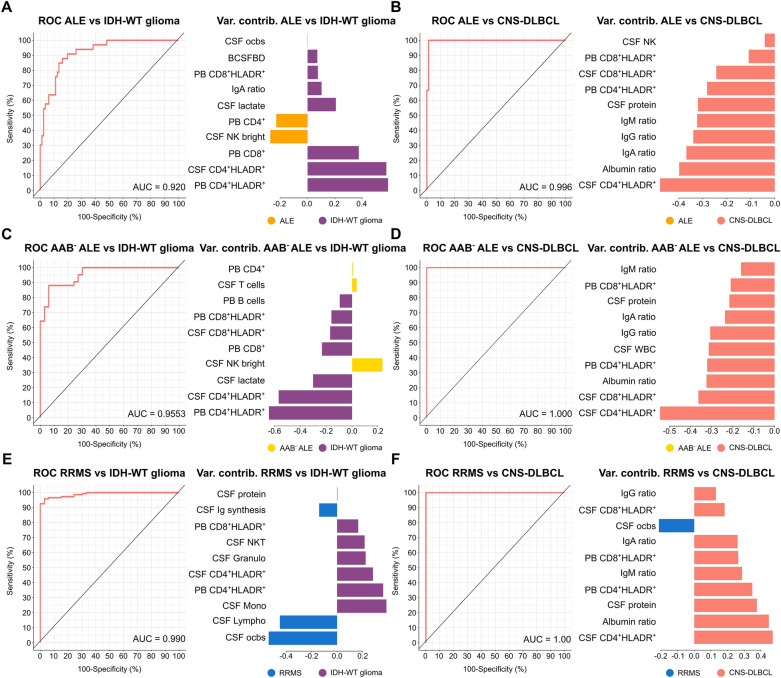
Fig. 3.
CSF routine together with PB and CSF mFC parameters can reliably differentiate ALE and RRMS patients from patients with primary CNS tumors. A–F ROC analyses of the classification results obtained from sPLS-DA including CSF routine, PB and CSF mFC parameters. ALE patients (A and B), antibody-negative ALE patients (C and D), or RRMS patients (E and F) were compared to either IDH-WT glioma or CNS-DLBCL. Loading plots visualize the top 10 variables contributing to latent component 1. Colors indicate the group in which the median is maximum. AAB− ALE antibody-negative ALE, ALE autoimmune limbic encephalitis, AUC Area under the curve, BCSFBD blood-CSF barrier dysfunction, cMono classical monocytes, CSF cerebrospinal fluid, CNS-DLBCL diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the central nervous system, contrib contribution, IDH isocitrate dehydrogenase wildtype glioma, Granulo granulocytes, iMono intermediate monocytes, Lympho lymphocytes, mFC multidimensional flow cytometry, Mono monocytes, ncMono non-classical monocytes, NK natural killer cells, NKT Natural killer T cells, PB peripheral blood, ocbs oligoclonal bands, Q ratio, ROC receiver operating characteristic, RRMS relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, SD somatic symptom disorder, sPLS-DA Sparse Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis, Var variable WBC white blood cell count, WT wildtype