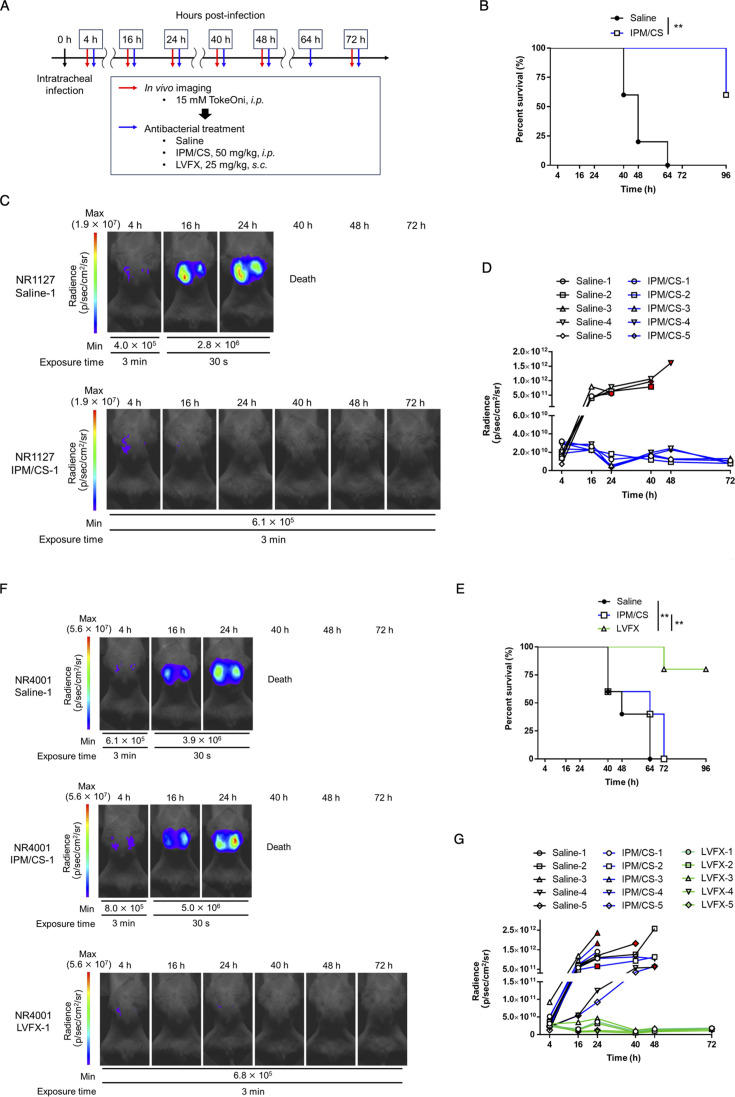
Fig 4.
Evaluation of the number of lung-colonizing bacteria of A. baumannii clinical isolates and its application to the assessment of the therapeutic efficacy of antimicrobial agents. Clinical isolates of A. baumannii (NR1127-Luc, a carbapenem-sensitive strain, and NR4001-Luc, a carbapenem-resistant strain) were intratracheally administered to immunodeficient mice at 5 × 107 and 1 × 108 CFU/mouse, respectively. TokeOni was then administered intraperitoneally for in vivo imaging, and saline (i.p.), imipenem/cilastatin (IPM/CS) (i.p.), or levofloxacin (LVFX) (s.c.) was administered for treatment at the indicated time points post-infection. Experiments were performed using five mice per group (A). Kaplan–Meier plot of the NR1127-Luc strain (B) and NR4001-Luc strain (E). Representative images of the NR1127-Luc strain (C) and NR4001-Luc strain (F) acquired using in vivo imaging. The signal obtained from all images of the NR1127-Luc strain (D) and NR4001-Luc strain (G) was plotted for each time point. Red symbols represent the results at the final imaging time points.