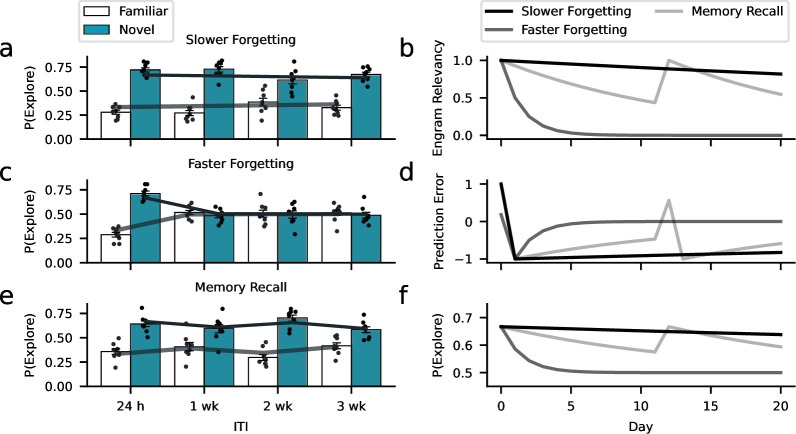
Figure 8. Learning model captures the dynamics of forgetting.
Environmental, optogenetic, and pharmacological manipulations might modulate the speed of forgetting by altering key parameters of our model. Simulations with different learning-rate parameters explain the forgetting dynamics of the different experimental conditions. (a) The enrichment and Rac1-inhibition conditions were successfully captured using a low learning rate (0.01, similar to the empirical estimates). (c) In contrast, assuming a larger learning rate (0.5), we could capture faster forgetting as observed in the Rac1 activator and context-only conditions. (e) Moreover, improved memory performance after reminder cues can be explained by assuming that these interventions induce a positive prediction error boosting object relevancy. Here, we assumed a learning rate of 0.07 (based on the empirical estimate). (b) Development of engram relevancy and (d) prediction errors across conditions. (f) Probability of exploring the novel object plotted separately for each condition.