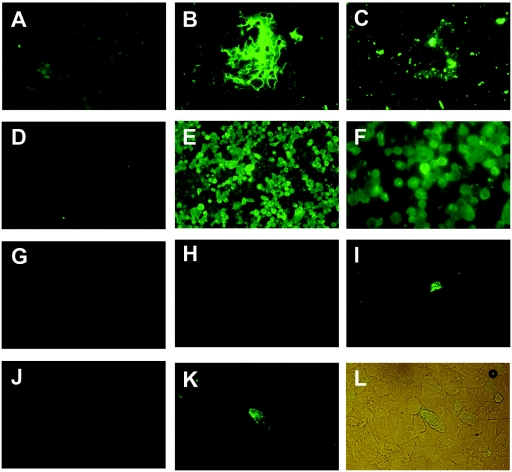
FIG. 1.
Detection of SARS-CoV in the cells derived from throat wash samples of SARS patients by an indirect immunofluorescence assay. (A to C) Untreated (A and B) and NAC-treated (C) cells derived from throat wash samples from a healthy control were incubated with 1× PBS (A) or anti-mucin 5AC monoclonal antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) (B and C), followed by FITC-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G. (D and E) SARS-CoV-infected Vero E6 cells were incubated with preimmune (D) or postimmune (E and F) serum from a rabbit immunized with the recombinant nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV (5), followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G. (F) Magnification (×400) of panel E. (G to L) NAC-treated cells of throat wash samples from a healthy control (G) and two patients (H to K) were incubated with the preimmune (H and J) or postimmune (G, I, and K) rabbit serum described above. (L) Light microscopic picture of panel K, taken with the fluorescent light on.