Fig. 3. R1R2 domains of E3/49K and its VHH mimics are sufficient to downregulate T cells.
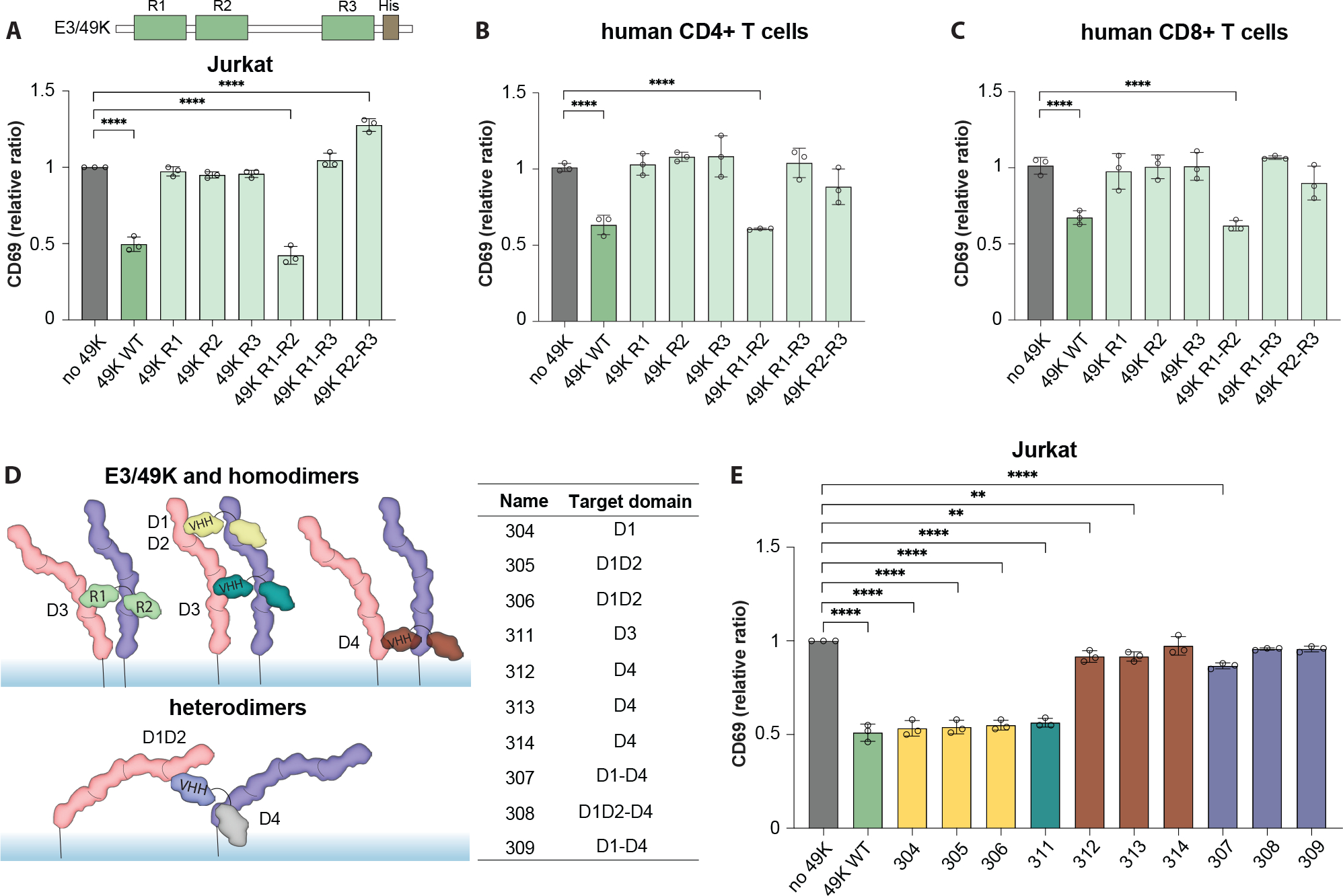
(A) (top) Cartoon representation of E3/49K construct and its R1-R3 domains. (bottom) CD69 expression upon incubating with different combinations of linked E3/49K domains, then stimulating with OKT3. (B) Same constructs tested in PBMC CD4+ T cells and (C) CD8+ T cells. (A-C), Data are mean ± s.d. from n = 3 replicates from different donors. Statistical significance is determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD multiple comparison test, (ns > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (D) (left) Cartoon representation of R1-R2 dimerizer and its VHH mimics binding to different domains of CD45 and inducing different conformations. (right) Table detailing targeted CD45 domains by each tested VHH mimic. (E) CD69 expression upon pretreatment with different VHH mimics then stimulated with OKT3 in Jurkat T cells. Data are mean ± s.d. from n = 3 replicates. Statistical significance is determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD multiple comparison test (ns > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001).
