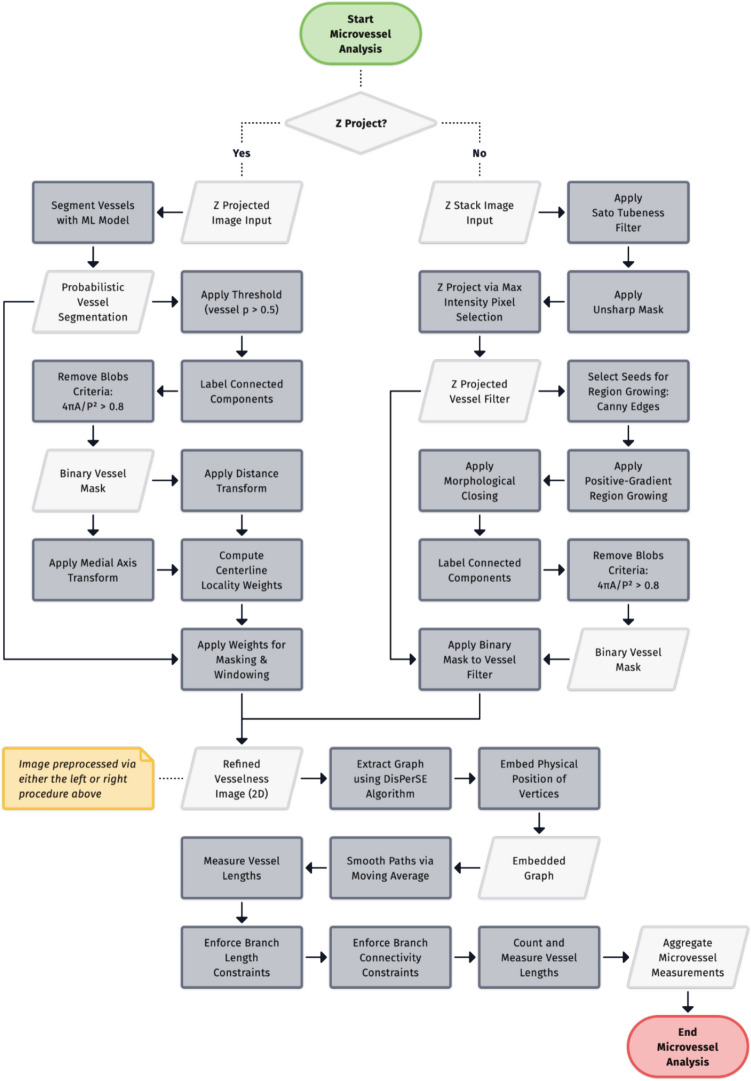
Fig. 3.
Workflow of the microvessel analysis pipeline. Input Z projections are segmented using a machine learning model, while input Z-stacks are filtered using a Sato tubeness filter. Either pathway produces a refined vesselness image, from which a graph representation is extracted using the DisPerSE algorithm. The resulting graph is then analyzed to measure vessel lengths. Branch length constraints are then applied and disconnected branches are then optionally removed. The pipeline outputs aggregate measurements of the microvessel network, including branch counts, average branch length, and total network length.