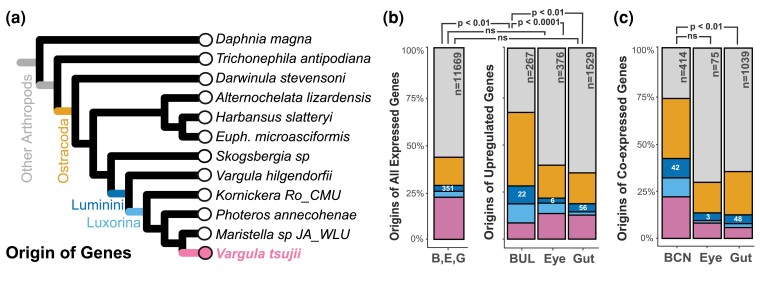
Fig. 5.
The contribution of novel and conserved genes co-expressed in the BCN and significantly upregulated genes uniquely expressed in the BUL, compound eye, and gut of V. tsujii restricted to V. tsujii, Luxorina, Luminini, Ostracoda, and Arthropoda. Conserved ostracoda/arthropoda genes dominate the set of genes in each dataset. a) Phylogeny of bioluminescent and nonbioluminescent ostracods and representatives of other arthropods are used to determine the origin of genes. b) Compared with the complete set of genes differentially expressed (minimum of two counts or more across biological replicates), only the upregulated genes of the BUL were characterized by a significantly higher proportion of Luminini-specific genes. Statistically significant pairwise comparison between BUL:B, E, G Dataset is indicated by P < 0.01. Statistical significance for pairwise comparisons between B, E, G (BUL, Eye, and Gut) Dataset, and tissue types was corrected for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni method. Compared with the proportion of the total number of Luminini genes upregulated in the compound eye and gut, the BUL had a significantly higher proportion of Luminini genes compared with the gut and compound eye. Statistically significant pairwise comparisons between BUL:Eye and BUL:Gut are indicated by P < 0.0001 and P < 0.01, respectively. c) Compared with modules expressed in the compound eye and gut, the BCN contains a higher proportion of Luminini genes, though not statistically significant in the compound eye. Statistically significant pairwise comparison between BUL:Gut module is indicated by P < 0.01. The bar plot represents the proportions as percentages, while the raw numbers are displayed inside the colored bars, with n indicating the total number. B/BUL, bioluminescent upper lip; E, compound eye; G, gut.