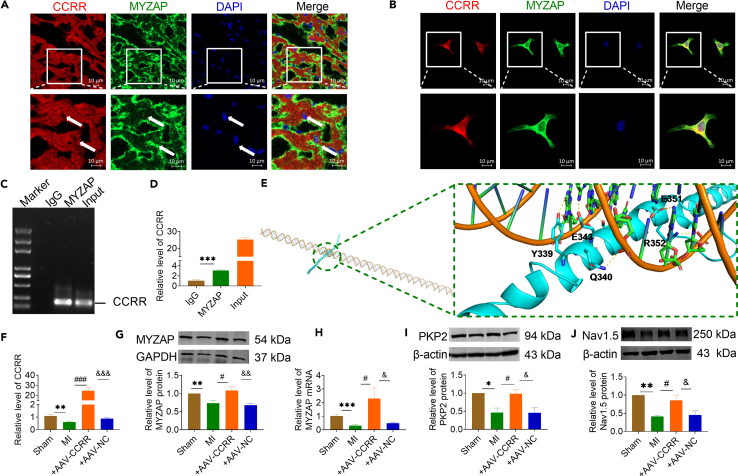
Figure 3.
CCRR regulates the expression of MYZAP, PKP2 and Nav1.5
(A and B) FISH and immunofluorescence staining were employed to examine co-localization of CCRR with MYZAP. CCRR was stained red, MYZAP was stained green, and nucleus were stained blue (A, n = 30, B, n = 28 visions). A, from mouse atrial tissue. B, from primary cultured atrial cardiomyocytes. Scale bar: 10 μm.
(C and D) RIP experiment detected the interaction between CCRR and MYZAP (n = 3 mice/group).
(E) CCRR-FD is constructed, the interaction between CCRR-Functional domain and MYZAP is predicted via the website (http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn/), and the interaction site is predicted using Pymol.
(F) Real-time PCR was used to detect the expression of CCRR in atrial cardiomyocytes (n = 6 mice/group).
(G) The expression of MYZAP in atrial tissue was detected by western blot. The expression of MYZAP in MI group was significantly lower than that in Sham group. MYZAP expression was significantly upregulated by AAV-CCRR compared with AAV-NC group (n = 6 mice/group).
(H) Real-time PCR results showed that MYZAP expression was decreased, which were reversed by overexpression of CCRR (n = 5 mice/group).
(I) Western blot was used to detect the expression of PKP2 protein. Compared with Sham group, the expression of PKP2 in MI group was significantly decreased, which was restored by AAV-CCRR compared to AAV-NC group (n = 6 mice/group).
(J) The protein expression of Nav1.5 was detected by western blot. Compared with Sham group, the expression of Nav1.5 was significantly decreased in MI group. Compared with AAV-NC group after MI, AAV-CCRR significantly restored the expression of Nav1.5 protein (n = 6 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. #p < 0.05, and ###p < 0.001. &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01, and &&&p < 0.001 (One-way ANOVA).