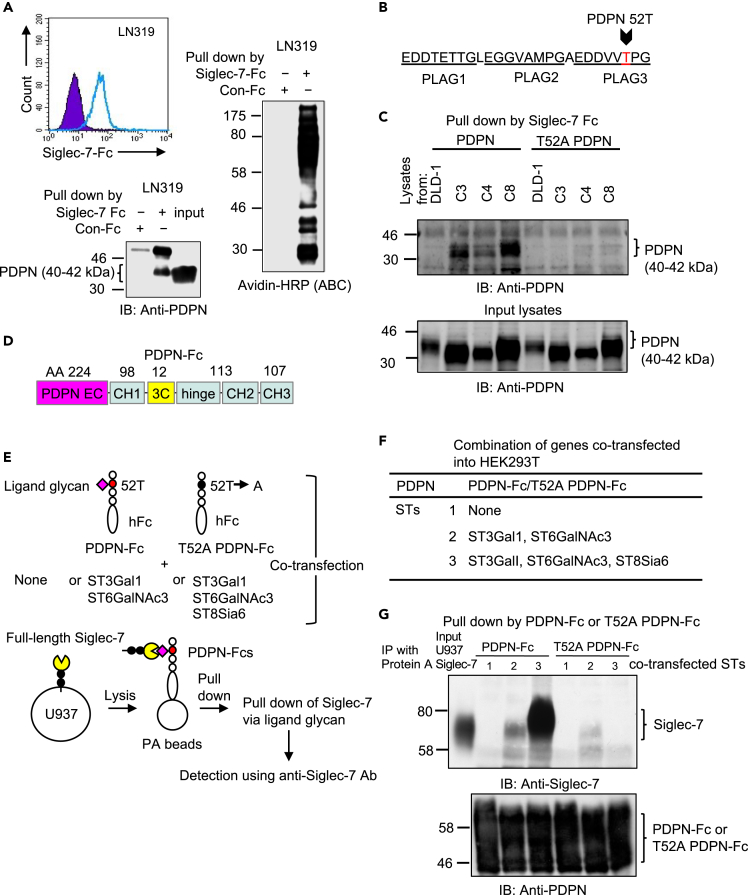
Figure 5.
Siglec-7 ligand-glycan is present at 52T on PLAG3 domain of PDPN
(A) PDPN was identified as a Siglec-7 ligand glycan-carrier protein in glioblastoma LN319. Flow cytometry showed that LN319 expresses Siglec-7-Fc binding molecules (upper). A pull-down assay of biotinylated proteins revealed that there were various types of membrane proteins binding to Siglec-7 (right). One of them was identified as PDPN using IB (lower).
(B) Identification the of Siglec-7 ligand glycosylation site. Di-sialyl T antigen is present in glycosylation products at 52T on the PLAG3 domain of PDPN.
(C) The wild-type and a point mutant of PDPN-expression vectors were used to transfect DLD-1 and its ST transfectants. Their PDPNs were pulled-down using Siglec-7-Fc from the lysates of DLD-1 and its ST transfectants, and analyzed using IB, showing that WT PDPN derived from DLD-1 did not bind to Siglec-7-Fc. WT PDPN derived from ST transfectants bound to Siglec-7-Fc. T52A PDPN derived from either DLD-1 or ST transfectants did not bind to Siglec-7.
(D) Generation of fusion protein (PDPN-Fc) consisting of the WT and T52A PDPN extracellular (EC) domain and human IgG-Fc.
(E) Evaluation of Siglec-7 binding ability to PDPN-Fc co-transfected with various STs. WT and T52A PDPN-Fcs were prepared by co-expression with none or ST3Gal1 and ST6GalNAc3 or ST3Gal1, ST6GalNAc3 and ST8Sia6 in HEK293T cells, and purified using the protein A affinity column. U937 cells expressing full-length Siglec-7 were lysed and purified and PDPN-Fcs were added to the lysates. PDPN-Fcs were pulled-down with Protein A beads, and the amount of co-precipitated Siglec-7 was compared. A T52A point mutant of PDPN-Fc in the PLAG3 domain was also generated under the same conditions.
(F) A list of co-transfected PDPN-Fc and STs.
(G) Binding of WT full-length Siglec-7 and PDPN-Fcs was detected using IP with the Fc fusion proteins and subsequent IB with anti-Siglec-7 (top). Expression of PDPN-Fc or its mutant was confirmed using IB with an anti-PDPN antibody (bottom).