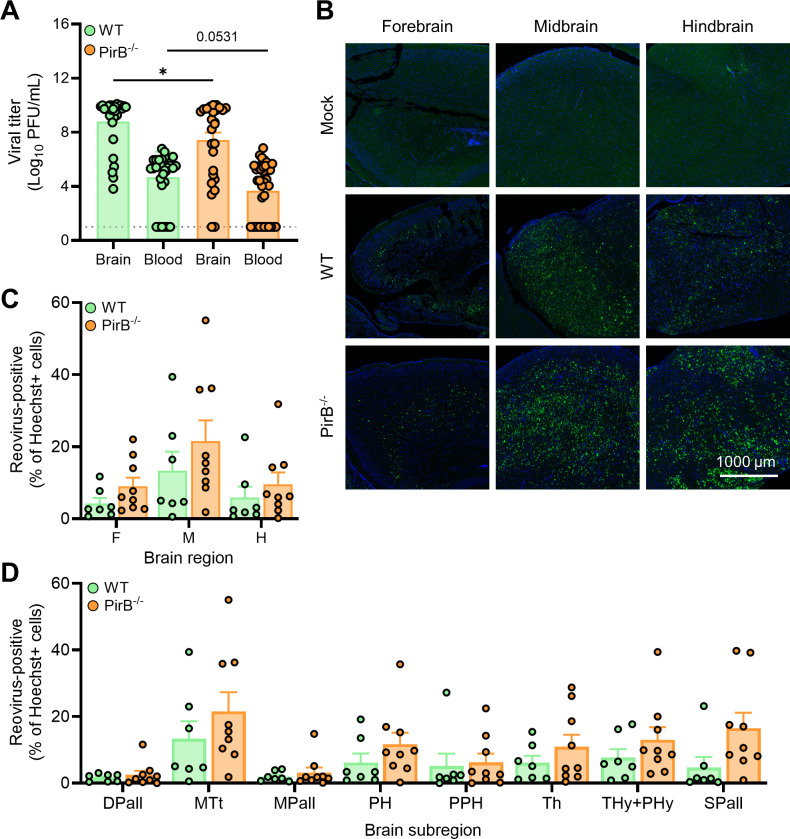
Fig 6.
PirB expression does not dictate reovirus infection patterns in the brain. (A–D) Two-to-three-day-old WT or PirB-/- mice were inoculated IC with phosphate-buffered saline (mock) or 200 PFU of reovirus strain T3SA−. Mice were euthanized at 7–8 days post-inoculation, and brain tissue and whole blood were collected. (A) Titers of the virus in the homogenized left-brain hemisphere and blood were determined by plaque assay. Each symbol represents the viral titer from an individual animal. Brain, N = 28/27 (WT/PirB-/-); blood, N = 31/35 (WT/PirB-/-). Error bars indicate SEM. Values that differ significantly from WT by unpaired t test are indicated (*P < 0.05). Dotted line indicates limit of detection. (B–D) Right-brain hemispheres (with contralateral hemisphere viral load between 4.17e8 and 1.4e10) were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned sagittally. Tissue sections were probed for reovirus RNA by HCR, counterstained with Hoechst dye, and imaged using a Lionheart FX automated imager. (C) Representative images are shown. Reovirus RNA is depicted in green; nuclei are depicted in blue. Scale bar, 1,000 µm. (C and D) Reovirus infection in established ROIs. Infection foci (HCR-positive) from each region (C) or subregion (D) of mock-infected and reovirus-infected mouse sections were enumerated using the Spot Detector tool within Icy software. Data are presented as the percentage of infected cells, wherein a reovirus-positive cell was determined by signal intensity greater than background defined using a mock-infected brain. N = 7/9 (WT/PirB-/-). Error bars indicate SEM. Values that differ significantly from WT by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test are indicated. DPall, dorsal pallium; MTt, collicular midbrain tectum; MPall, medial pallium; PH, pontine hindbrain; PPH, prepontine hindbrain; Th, thalamus; Thy+PHy, hypothalamus; and SPall, subpallium.