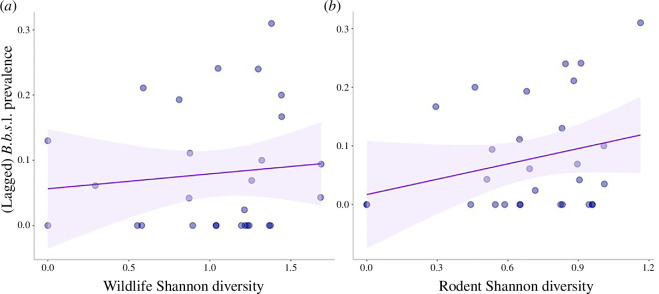
Figure 3.
(a–b) Northern California. Wildlife and rodent Shannon diversity were the only predictive metrics for Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. (B.b.s.l.) nymphal infection prevalence (NIP). Wildlife diversity was measured as the relative count index of large vertebrates captured with wildlife camera traps, and rodent diversity was measured with a live trapping mark and recapture study. Both variables were positively correlated with Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. prevalence amongst I. pacificus nymphs, lagged by 1 year.