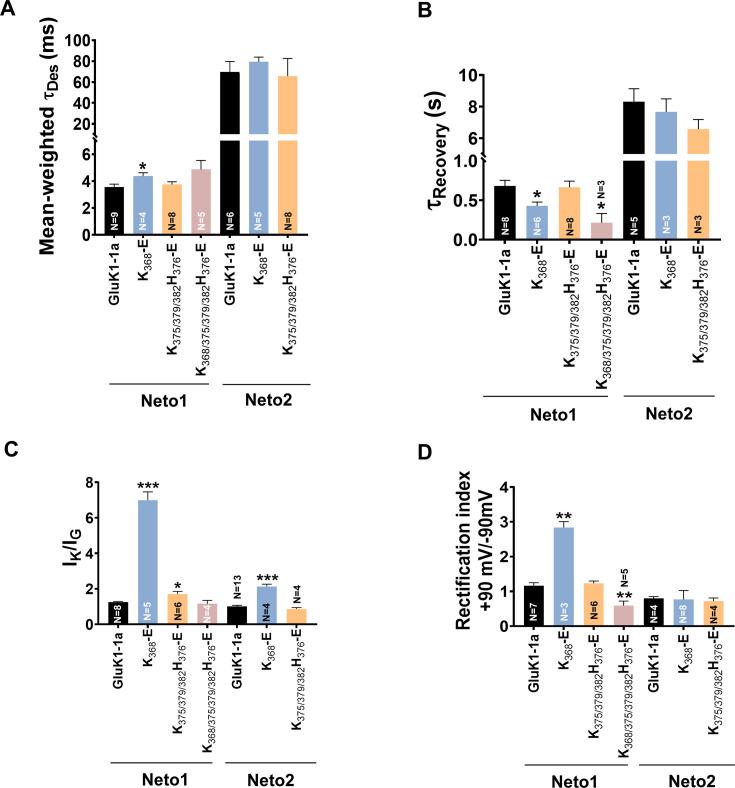
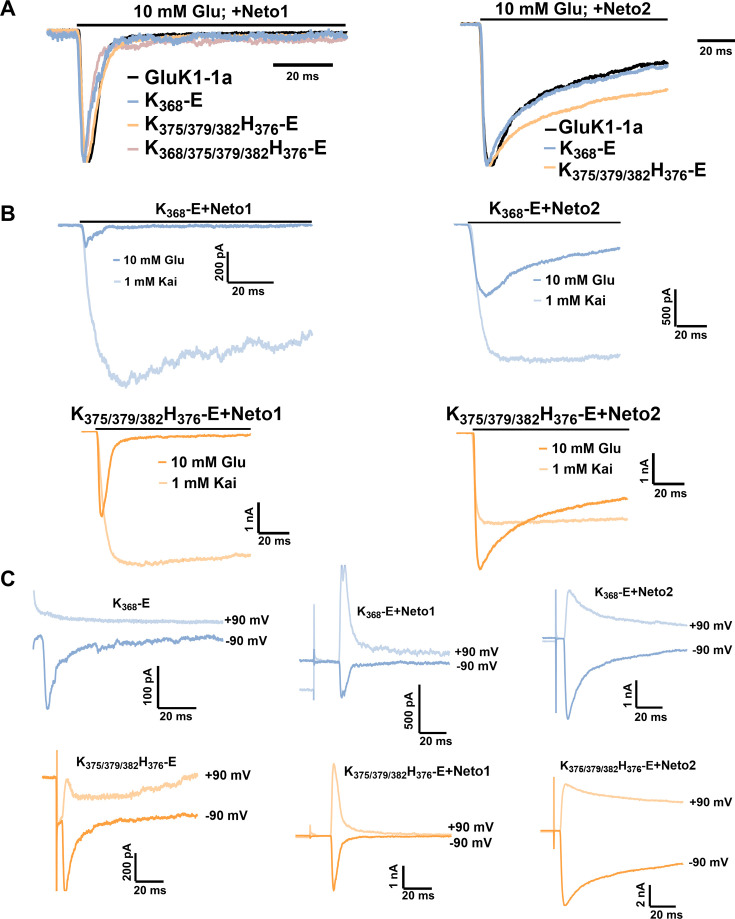
Figure 5. Mutation of GluK1-1a splice insert residues affects the receptor modulation by Neto proteins.
Bar graphs (mean ± SEM) show a comparison between wild-type and mutant receptors with Neto proteins for different kinetic properties. (A) Mean-weighted Tau (τDes) values for GluK1-1a wild-type and mutant receptors in the presence of 10 mM glutamate and expressed with Neto1/2. (B) Tau (τRecovery) recovery values for GluK1-1a and mutants with Neto1/2. (C) The ratio of the peak amplitudes evoked in the presence of 1 mM kainate and 10 mM glutamate for GluK1-1a mutants co-expressed with Neto1/2 is shown. (D) The rectification index represented by the ratio of currents evoked by 10 mM glutamate application at +90 mV and –90 mV for the wild-type and mutant receptors with Neto proteins is shown. The wild-type GluK1 splice variants’ data is the same as in Figure 2 and is replotted here for comparison. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM, N in each bar represents the number of cells used for analysis, and * indicates the significance at a 95% confidence interval.