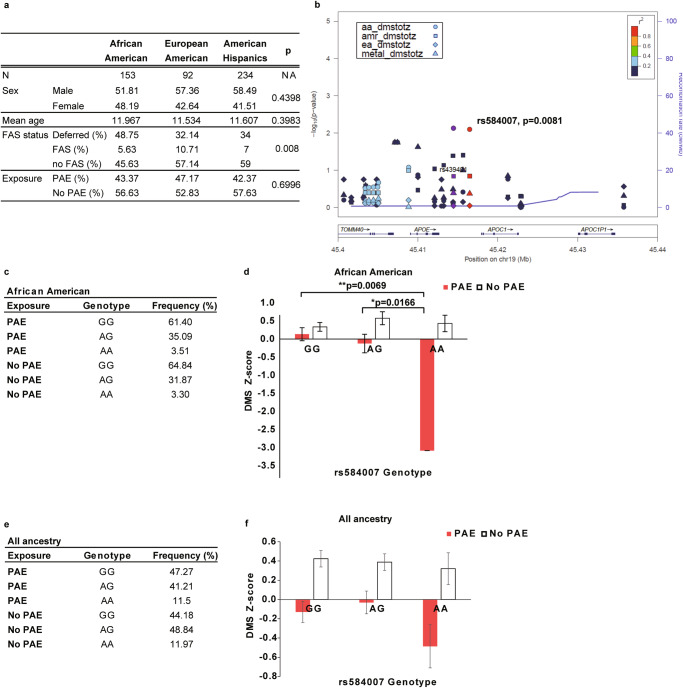
Fig. 5. The SNP rs584007 in an ApoE enhancer is associated with DMS Z-score in PAE children.
a Table shows demographic information on study subjects. No significant differences are found in the gender ratio and mean age between the three ancestry groups by Chi-square test and one-way ANOVA, respectively. A significant difference in fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) diagnosis, but not in the number of PAE individuals, is observed between the ancestry groups by Chi-square test. NA = not applicable. b Regional plot between 45.4 and 45.44 Mb on chromosome 19 around the APOE locus in the African (aa), American Hispanic (amr), and European (ea) ancestries and meta-analysis (metal) of GWAS with DMS Z-score. The interaction between SNP and PAE shows a significant association with the DMS z-score in the group of African American ancestry. c Table indicates the frequency of individuals with the rs584007 genotype in the African American ancestry group. d In the group of African American ancestry, AA individuals prenatally exposed to alcohol have significantly lower DMS Z-scores compared to individuals with other genotypes with or without exposure to alcohol. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA with simple main effect test. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. e Table indicates the frequency of individuals with the rs584007 genotype in all ancestry groups. f When all ancestry groups are combined, no significant interaction between PAE and SNP is observed by two-way ANOVA (P = 0.3769). A significant alcohol effect is observed (P < 0.0001). There is a marginal difference in the DMS Z-score between AA and other genotypes in alcohol exposed groups (AA vs GG P = 0.09937; AA vs AG P = 0.0991 by Tukey’s post hoc test). Data represent mean ± s.e.m.