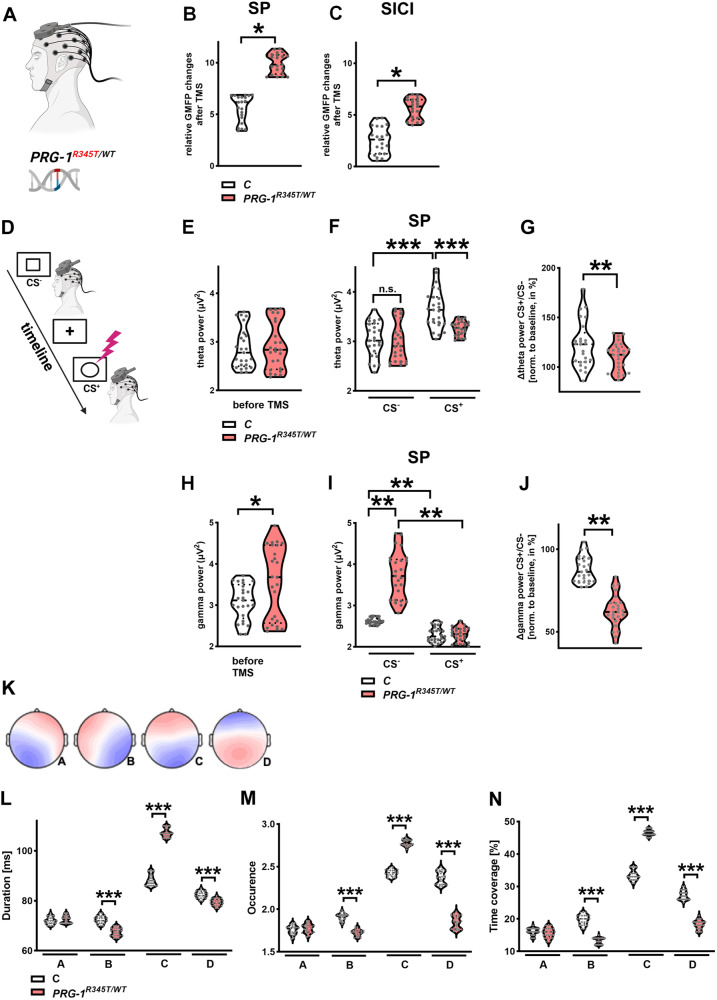
Fig. 1. Cortical network excitability shows significant dynamic alterations in PRG-1R345T/WT mutation carriers.
A Experimental design for the assessment of excitability changes and E/I balance shifts in the frontal cortex of PRG-1R345T/WT carriers using high-density EEG and TMS stimulation of the dmPFC. B SP: Global mean field potential (GMFP) over frontal cortex after single TMS-pulses (SP) over the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) was significantly increased in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to age and sex matched control subjects (n = 25). C SICI: After inhibitory Double TMS-pulses (SICI) over the dm PFC, GMPF over the frontal cortex in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) was lower when compared to values after single pulse, however, it was significantly higher than in control subjects (n = 25). D Experimental design of the instructed fear paradigm. Unconditioned/safety Stimulus (CS-) or a conditioned stimulus (CS+), which in 1/3rd of presentations was accompanied by an electric shock, were presented for 5 s following an image of a fixation cross (5–6 s). Single-pulse TMS was applied on the dmPFC 1 s after presentation of each stimulus. E Global theta power over frontal cortex at baseline was not altered in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to matched control subjects (n = 25). F Theta power over the frontal cortex was not different between control subjects (n = 25) and PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) following CS- presentation and single pulse TMS over dmPFC. However, following CS+ presentation and SP TMS, global theta power was significantly increased in control subjects, while a significant lower theta power was observed in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers under same conditions. G Theta power ratio of GMFP changes following SP with prior CS+ or CS- presentation (normalized to baseline theta power) displayed significantly reduced increase in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to control subjects (n = 25) under same conditions. H Global gamma power over the frontal cortex at baseline was significantly increased in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to matched controls (n = 25). I After CS-, TMS over dmPFC resulted in significantly higher gamma power over the frontal cortex in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to control subjects (n = 25). However, after presentation of a conditioned stimulus (CS+), gamma power was supressed and significantly lower in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers when compared to CS- conditions and was not different to control subjects. J Ratio of gamma power following SP with CS+ to SP with CS- (both normalized to baseline gamma power) showed higher supression of gamma power in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) following CS+ when compared to control human subjects (n = 25) under same conditions. Data in A-J are represented as violin plots covering all individual data points. Median, lower and upper quartiles are shown by dotted lines (* and ** show group differences of * >80% or **>90%, Bayesian analysis). K. Spatial configuration of the four microstate classes (A, B, C, D) according to EEG analyses. L–N EEG-analyses of the temporal microstates parameters for mean duration (shown in L), occurrence (shown in M) and time coverage (shown in N) revealed significant increases in microstate (C) and reduction in microstates (B, D) in PRG-1R345T/WT carriers (n = 25) when compared to control subjects (n = 25). Age and gender were calculated as covariates. Analyses were performed using Bayesian one-way ANOVA. *** represent highest significance for Bayes factors >100. Data is shown as violin plots covering all individual data points. Median, lower and upper quartiles are shown by dotted line.