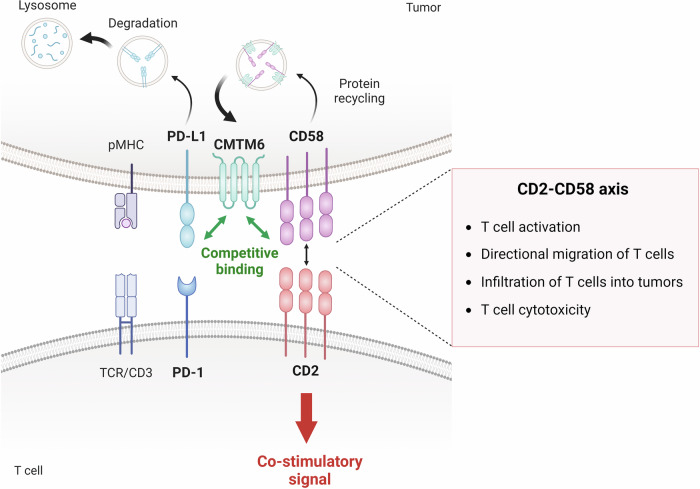
Fig. 3. Regulation of tumor immunity and immune evasion via the CD2‒CD58 axis.
CD58 downregulation on tumor cells is associated with resistance to cancer treatments such as ICI and CAR T-cell therapies. At the molecular level, this occurs when PD-L1 competes with CD58 for binding to extracellular loops within the MARVEL domain of CMTM6, leading to the downregulation of CD58 by promoting its lysosomal degradation instead of endosomal recycling. This increase in PD-L1, resulting from the loss of CD58, contributes to tumor immune evasion. In addition, impaired CD58 binding to CD2 on T cells hampers antitumor immune responses through various mechanisms, including reduced T-cell activation, directional migration, infiltration into tumors and cytotoxicity.