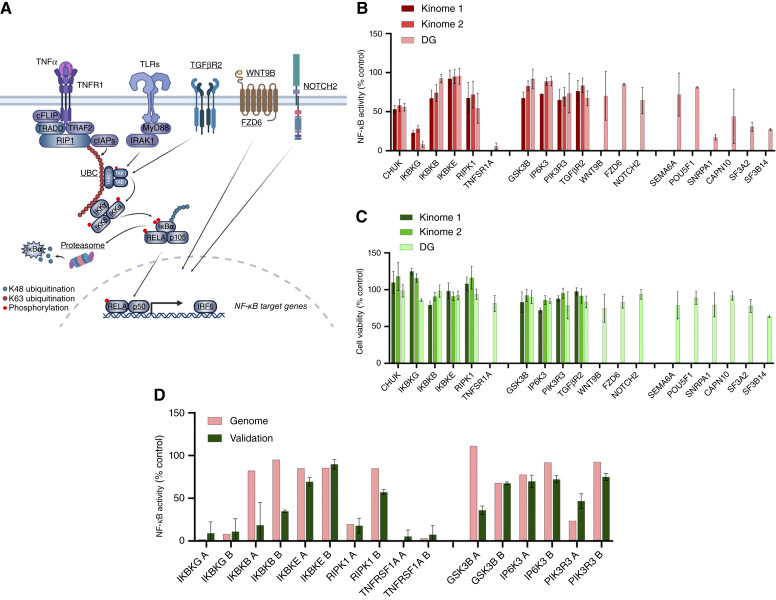
Figure 1.
RNAi screening identifies G2/M kinases and kinetochore components as modulators of TNFα-induced NF-κB reporter activity and cell viability. A, Schematic demonstrating identified canonical and noncanonical regulators of NF-κB from the RNAi screening. Identified hits are in bold and underlined. B, NF-κB reporter activity in UMSCC1κB after transfection with select siRNAs from the kinome 1, kinome 2, and DG RNAi screens. Canonical and noncanonical hits are shown. NF-κB activity is shown as a percentage of a negative control siRNA (set at 100%). C, Cell viability in UMSCC1κB after transfection with select siRNAs from the kinome 1, kinome 2, and DG RNAi screens. Canonical and noncanonical hits are shown. Cell viability is shown as a percentage of a negative control siRNA (set at 100%). D, Validation of NF-κB reporter activity in UMSCC1κB comparing primary and secondary screen with three independent siRNAs. Select siRNAs from the RNAi screen are shown compared with the DG results (Genome in figure). Canonical and noncanonical hits are shown. NF-κB activity is shown as a percentage of a negative control (set at 100%). Each RNAi screen contained three individual siRNA targeting each gene. Validation siRNA experiments used separate siRNAs not used in the RNAi screens. (A, Created with BioRender.com.)