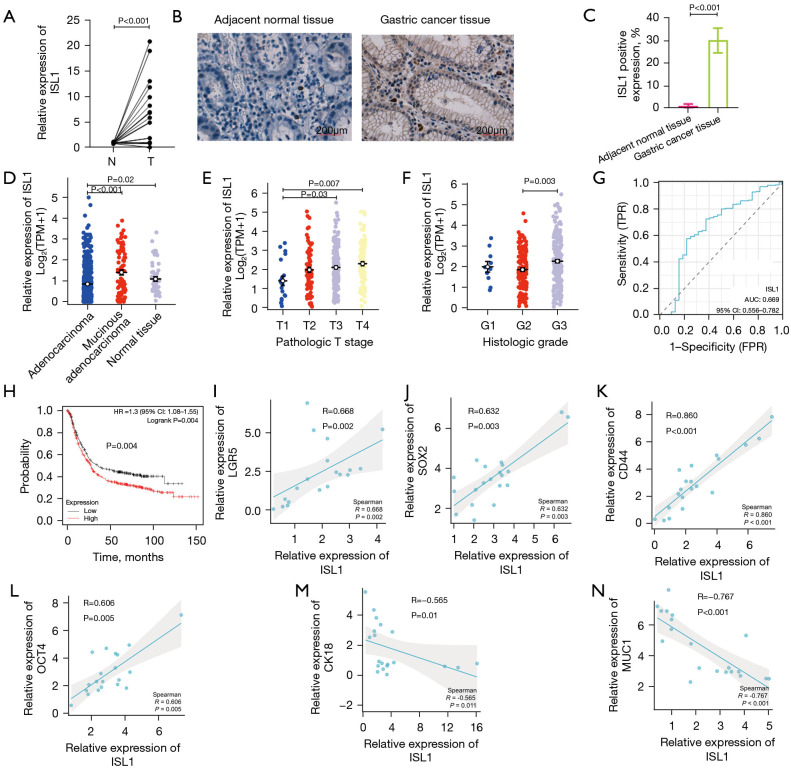
Figure 1.
Expression of ISL1 in patients with gastric cancer. (A) Expression levels of ISL1 were measured in GCs and matched GMs (Cohort 1, n=12, log-rank test, two-sided). (B,C) Immunohistochemistry was used to detect ISL1 expression in tissues and the rate of ISL1 positivity per high magnification field of view was counted. (D-F) Expression of ISL1 in patients with different gastric cancer types in the TCGA database. (G) ROC curves were established to test the discriminative value of ISL1 for gastric cancer tissues. (H) Survival curves of OS between ISL1-high and -low patients with gastric cancer. (I) The correlation of ISL1 and LGR5 mRNA expression. (J) The correlation of ISL1 and SOX2 mRNA expression. (K) The correlation of ISL1 and CD44 mRNA expression (biological repeat 3 times). (L) The correlation of ISL1 and OCT4 mRNA expression. (M) The correlation of ISL1 and CK18 mRNA expression. (N) The correlation of ISL1 and MUC1 mRNA expression. ISL1, insulin gene enhancer binding protein-1; N, normal tissue; T, gastric cancer tissue; TPM, transcripts per million; TPR, true positive rate; FPR, false positive rate; AUC, area under the curve; HR, hazard ratio; GCs, gastric cancer tissues; GMs, gastric mucosal tissues; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; OS, overall survival; LGR5, leucine rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5; SOX2, SRY-box transcription factor 2; CD44, CD44 molecule; OCT4, POU class 5 homeobox 1; CK18, keratin 18; MUC1, mucin 1. Pathological types of gastric cancer: adenocarcinoma, mucinous adenocarcinoma.