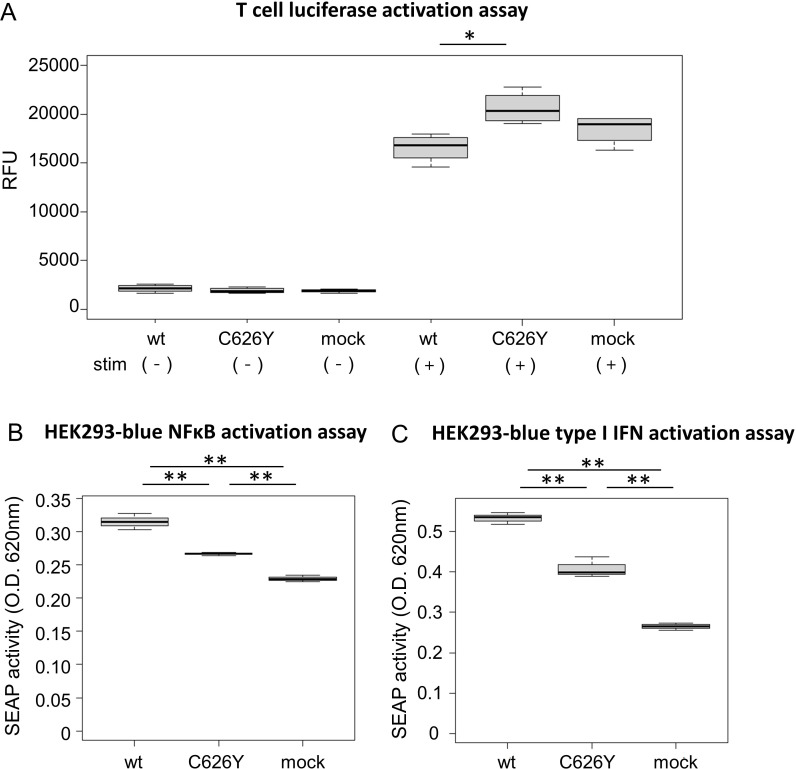
Figure 3.
Functional experiments of IKBKE variant transfected into reporter cells. (A) Jurkat-Lucia NFAT cells (Jurkat cells capable of detecting NFAT activation) were transfected with plasmids containing wild-type IKBKE or mutant IKBKE. After a certain period of cultivation, the transfected cells were collected using flow cytometry. After sorting, the NFAT activation levels of each cell under unstimulated conditions were shown on the left side of the figure, and the NFAT activation levels after CD3 and CD28 stimulation were shown on the right side of the figure. (B, C) NFκB and type I IFN activation was observed from HEK 293 reporter cells, [(B) Human TNF-α SEAP reporter HEK293 cells, (C) Human HEK293 cells - Type I IFNs reporter cells] transfected with plasmids containing wild-type IKBKE or mutant IKBKE. The activation of NFκB and type I IFN were quantitatively evaluated in the supernatant by measuring the amount of SEAP produced along with them in the reporter cells. (A) was experimented in quadruplicate, while (B, C) were experimented in triplicate. Pairwise comparisons using t-test with Bonferroni adjustment. IFN, interferon; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; SEAP, secreted alkaline phosphatase; wt. wild-type; O.D., optical density; RFU, relative fluorescence unit. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005.