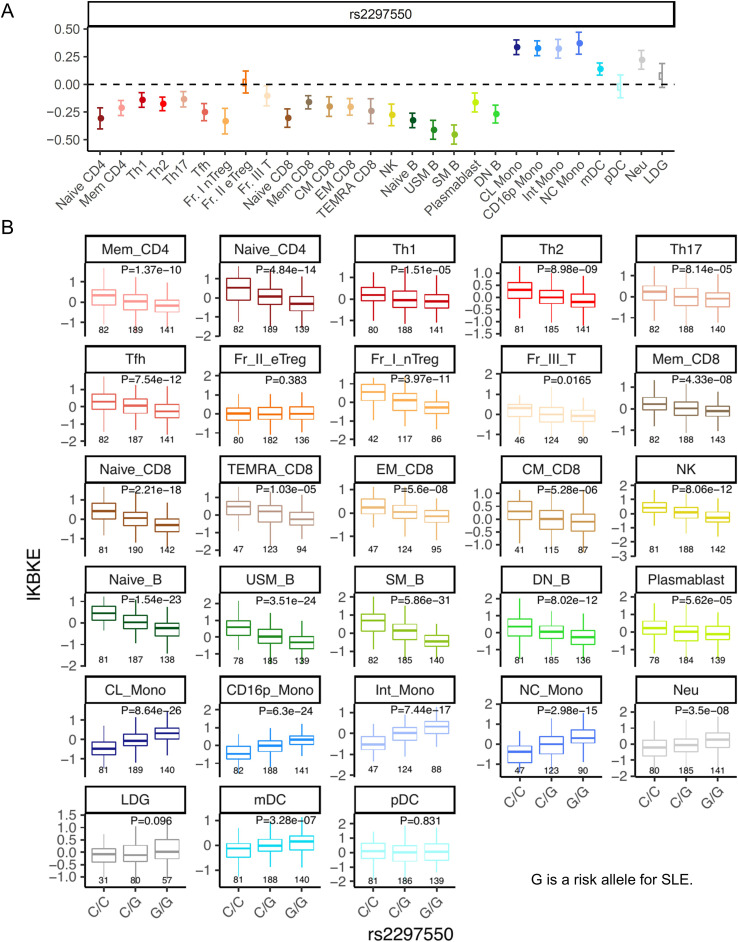
Figure 5.
eQTL analysis of the SLE risk IKBKE variant. (A) The cis-eQTL effect beta by this allele. A positive beta corresponds to an increase in gene expression due to the risk allele. The error bars represent the 95% confidence interval. (B) cis-eQTL effects boxplots on the expression of IKBKE across cell subsets. G is a risk allele for systemic lupus erythematosus. The p-value represents the association of eQTL (linear regression) p-values. Below the boxplot are the sample sizes for each group. Naïve CD4, Naïve CD4 T cells; Mem CD4, Memory CD4 T cells; Th1, T helper 1 cells; Th2, T helper 2 cells; Th17, T helper 17 cells; Tfh, T follicular helper cells; Fr. I nTreg, Fraction I naïve regulatory T cells; Fr. II eTreg, Fraction II effector regulatory T cells; Fr. III T, Fraction III non-regulatory T cells; Naïve CD8, Naïve CD8 T cells; CM CD8, Central memory CD8 T cells; EM CD8, Effector memory CD8 T cells; TEMRA CD8, CD8+ T effector memory CD45RA+ cells; NK,Natural killer cells; Naïve B, Naïve B cells; USM B, Unswitched memory B cells; SM B, Switched memory B cells; DN B, Double negative B cells; Plasmablast, Plasmablasts; CL Mono, Classical monocytes; CD16p Mono, CD16 positive monocytes, Int Mono, Intermediate monocytes; NC Mono, Non-classical monocytes; mDC, Myeloid dendritic cells; pDC, Plasmacytoid dendritic cells.