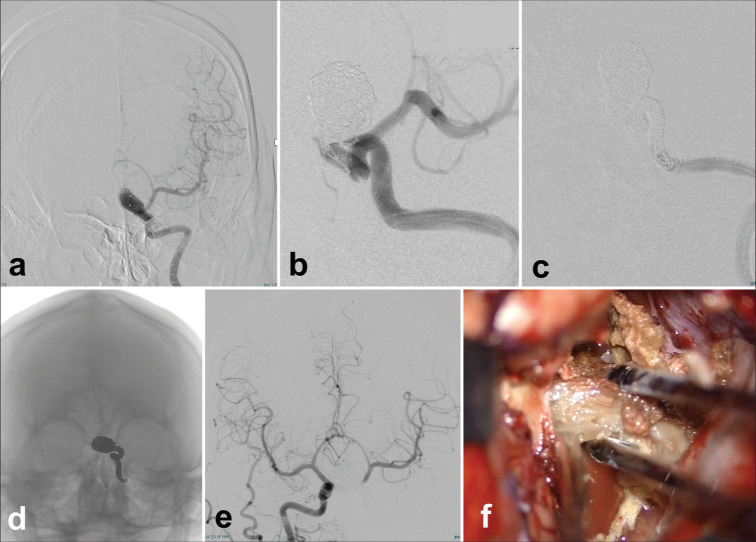
Figure 4:
Short-term two-stage operation for a patient with a thrombosed giant aneurysm of the left carotid artery. Endovascular parent artery occlusion of the affected artery (a-e) and decompressive partial removal of the giant thrombosed aneurysm through direct surgery (f). (a) A left internal carotid arteriogram shows a residual flow in the left carotid artery aneurysm and an upward-shifted left anterior cerebral artery (a). (b) Coil embolization was performed from the flow-residual part of the partially thrombosed aneurysm to the petrous portion of the left internal carotid artery (ICA). (c and d)The left ICA angiogram shows a complete occlusion from the aneurysm to the left proximal ICA. (e) A favorable distal flow of the left middle cerebral artery by the right ICA angiogram. (f) A decompressive removal of the aneurysmal thrombus was performed through left fronto-temporal craniotomy just after the low-flow bypass from the superficial temporal artery to the middle cerebral artery.