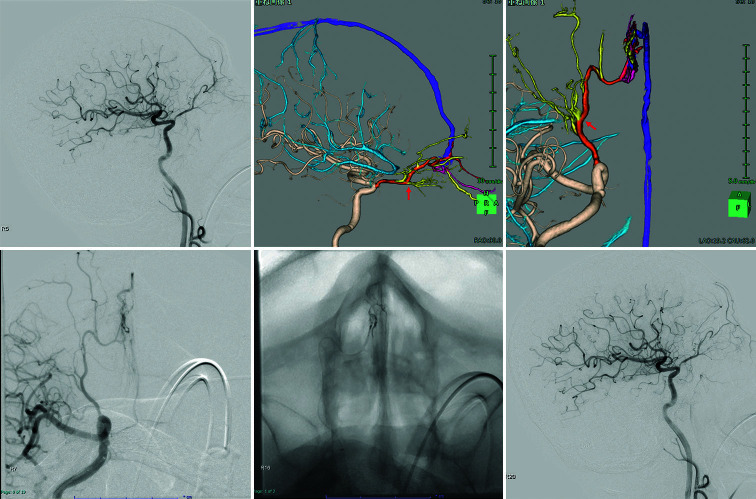
Figure 3:
(a) Digital subtraction angiography reveals anterior cranial fossa-dural arteriovenous fistula. (b and c) A three-dimensional (3D) reconstructed vascular image visually aids in understanding the 3D angioarchitecture of the shunt. The right posterior ethmoid arteries feed the shunt and drain the superior sagittal sinus through dilated cortical veins. Red arrow (b): Beginning of the central retinal artery. The right posterior ethmoidal artery (c; red arrow) is not tortuous and is close to the shunt point. (d and e) The front view shows the location of catheters navigated to the shunt through the right ophthalmic artery. The microcatheter is close to the shunt. The intermediate distal-access catheter is located in the ophthalmic portion of the right internal carotid artery. (f) The shunt point is completely occluded by backflow from the shunt pouch to each feeder, and the shunt disappears.