FIGURE 4.
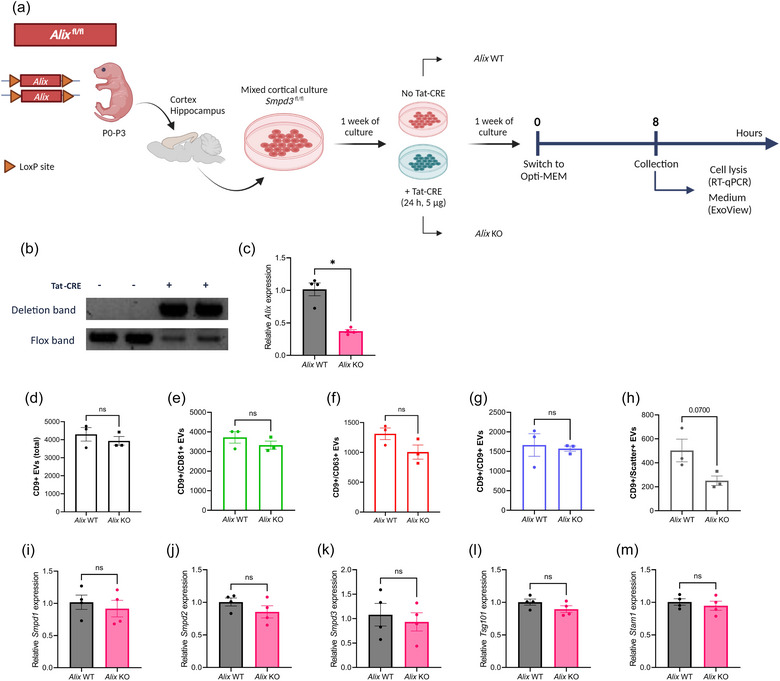
Alix deficiency in mixed cortical cell (MCC) cultures does not affect the level of EV production. (a) Schematic overview of the experimental set‐up for Alix fl/fl MCC culture, TAT‐CRE mediated Alix deletion and EV collection. (b) Deflox PCR on lysed MCC cells. The presence of the deletion band (473 bp) shows effective TAT‐CRE mediated ‘defloxing’. The flox band (368 bp) is less pronounced in Alix KO MCCs while clearly present in Alix WT MCCs. (c) Alix expression in Alix KO MCCs analyzed with RT‐qPCR, relative to Alix WT MCCs. (d–h) ExoView quantification of CD9+ EVs in MCC culture medium from Alix WT (n = 3) and Alix KO (n = 3) MCC cultures, showing the total (d), CD81+ (e), CD63+ (f), CD9+ (g) and label‐free scatter+ (50–200 nm) (h) EVs on the CD9 capture spot. (i–m) Expression level of Smpd1 (i), Smpd2 (j), Smpd3 (k), Tsg101 (l) and Stam1 (m) in MCCs from Alix WT (n = 4) versus Alix KO mice (n = 4). Results are represented relative to Alix WT MCC expression values. Data are represented as means ± SEM. Statistical comparison of two groups was performed by unpaired t‐testing or a Mann–Whitney test (*p < 0.05; ns, not significant). Alix, apoptosis linked gene 2 interacting protein X; EV, extracellular vesicle; MCC, mixed cortical cell; Smpd, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase.
