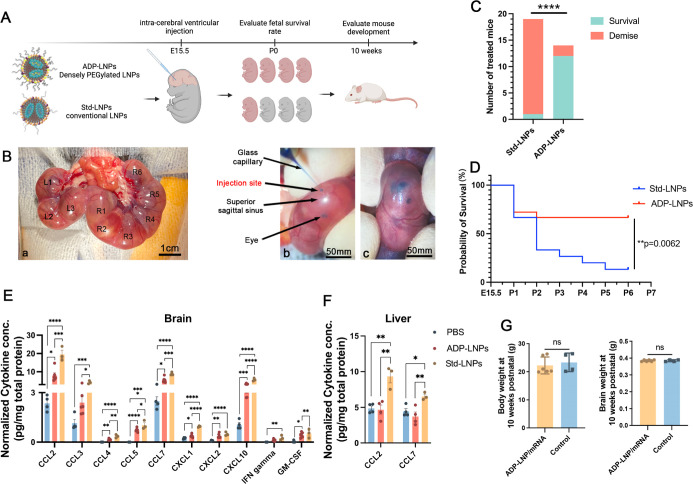
Figure 2.
In utero ICV delivery of ADP-LNPs is safe and well tolerated. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental protocol used to assess the safety of in utero ICV injection of ADP-LNPs and standard MC3-LNPs (Std-LNPs). (B) Intraoperative images showcasing the ICV injection procedure performed in utero. (a) All fetuses on either side of the uterine bifurcation (right or left) were noted; (b) a glass pipet was used to inject the LNPs into the fetal lateral cerebral ventricular space; and (c) successful injection into the ventricular system was determined by the spreading of the blue food dye into the ventricular zone (VZ). (C) Survival outcomes at birth for mouse fetuses subjected to LNP injections of either ADP-LNPs or Std-LNPs. ADP-LNP-treated fetuses had a significantly higher survival rate than fetuses treated with Std-LNPs (****p < 0.0001). (D) Kaplan–Meier survival curve of fetuses from E15.5 to postnatal day 7, comparing Std-LNPs and ADP-LNPs. ADP-LNPs demonstrated significantly higher survival probability (**p = 0.0062). (E,F) Normalized cytokine concentrations in brain (E) and liver (F) tissues 48 h postinjection exhibited significant differences between LNP-treated groups and the PBS control group 48 h postinjection. ADP-LNPs showed significantly lower cytokine levels compared to Std-LNPs, indicating reduced inflammatory response. (G) Body and brain weights at 10 weeks postnatal, comparing ADP-LNP/mRNA-treated mice and controls. No significant differences were observed, indicating normal postnatal development (data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 6 for the ADP-LNP/mRNA group and n = 4 for the PBS control group).