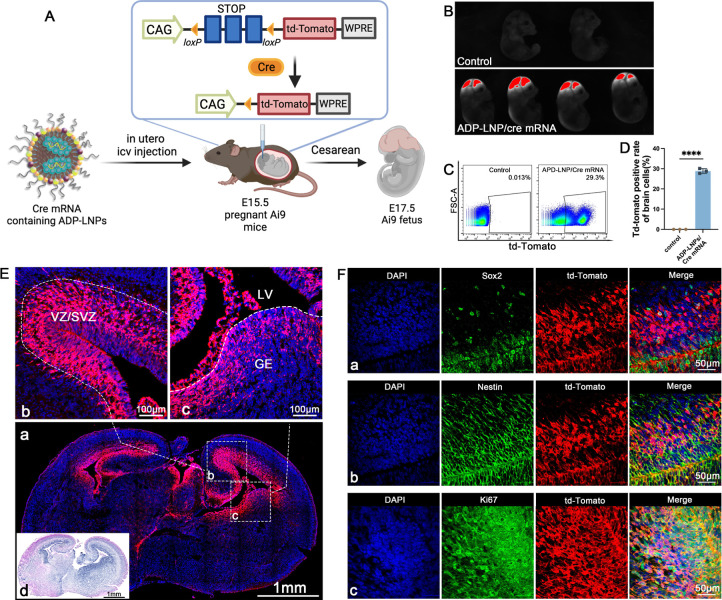
Figure 3.
ADP-LNPs efficiently deliver Cre mRNA in utero to Ai9 mice after an ICV injection. (A) Schematic describing the experimental protocol used to evaluate the transfection efficiency of Cre mRNA delivered by ADP-LNPs into the mouse brain in utero. Fetal Ai9 mice received ICV injections of LNPs on day E15.5 and were analyzed 48 h later on day E17.5. (B) Whole fetus imaging reveals significant td-Tomato expression in the brains and spinal cords of fetuses treated with ADP-LNP/Cre mRNA complexes, compared to the negligible background signal in PBS-treated control Ai9 mice, indicating efficient transfection. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of the fetal brain 48 h post ICV injection reveals an average transfection rate of 28.87 ± 0.69% (D) among total brain cells, demonstrating global transfection of the fetal brain (data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 3, ****p < 0.0001). (E) Histological examination of brain sections indicates that the majority of td-Tomato-positive cells are localized within the GE, VZ, and SVZ (a). Higher magnification image of the VZ, SVZ (b), and GE (c) showing extensive transfection in these proliferative regions. (d) H&E staining of an adjacent coronal section showing the overall brain structure for comparison. (F) Immunohistochemical staining further characterizes the td-Tomato-positive cells and demonstrates that most transfected cells are proliferating neural stem and progenitor cells (Sox2+/Nestin+/Ki67+), confirming that ADP-LNPs can efficiently transfect stem and progenitor cell populations within the fetal brain.