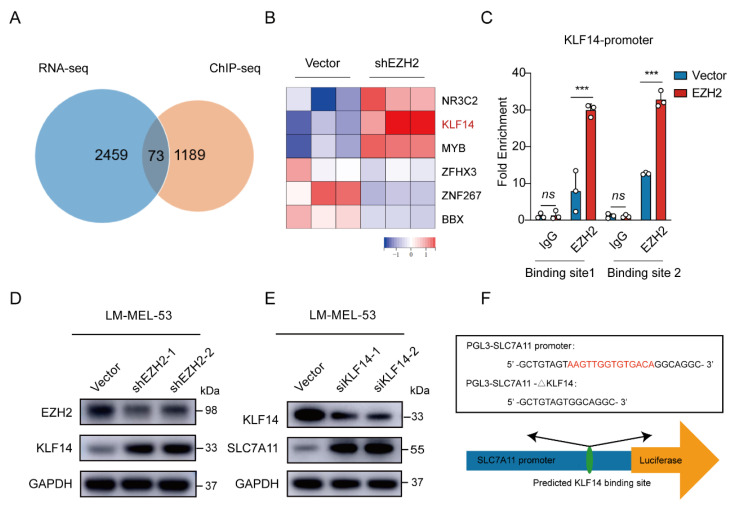
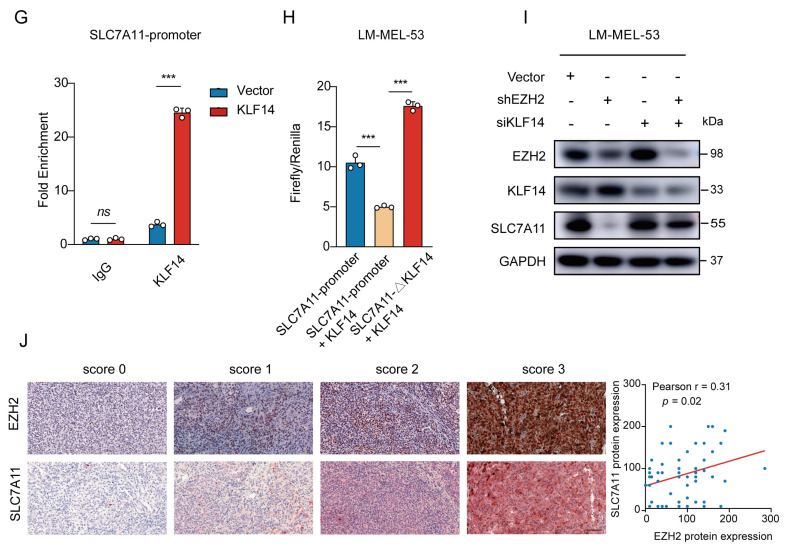
Figure 6.
EZH2-mediated SLC7A11 upregulation is regulated by KLF14. (A) Venn diagram of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq related genes showing that 73 genes were found to be potential target genes of EZH2. (B) Heatmap showing the 6 transcription factors of the 73 potential target genes of EZH2. (C) The binding of EZH2 to KLF14 promoter was detected after EZH2 overexpression by ChIP-qPCR. IgG as a negative control. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3, ns, not significant, *** p < 0.001. (D) The protein level of KLF14 was detected with EZH2 depletion. (E) The protein level of SLC7A11 after transfection of KLF14 siRNA. (F) Schematic representation of the predicted KLF14 binding site within the SLC7A11 promoter. (G) The binding of KLF14 to SLC7A11 promoter was detected after KLF14 overexpression by ChIP-qPCR. IgG as a negative control. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3, ns, not significant, *** p < 0.001. (H) Luciferase assay measuring SLC7A11 promoter activity before and after KLF14 binding site deletion in the absence or presence of KLF14. Luciferase activities were normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3, *** p < 0.001. (I) Western blot analysis of EZH2, KLF14, and SLC7A11 protein expression following dual knockdown of EZH2 and KLF14. (J) The correlations between EZH2 and SLC7A11 protein expression in MM patients were analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis (n = 55). Representative images from immunohistochemical staining of EZH2 and SLC7A11 protein expression. The staining score for each sample, counting the intensity of the staining, was graded as 0, 1, 2, and 3 (“0” as negative, and “3” as the strongest). Scale bar: 100 μm.