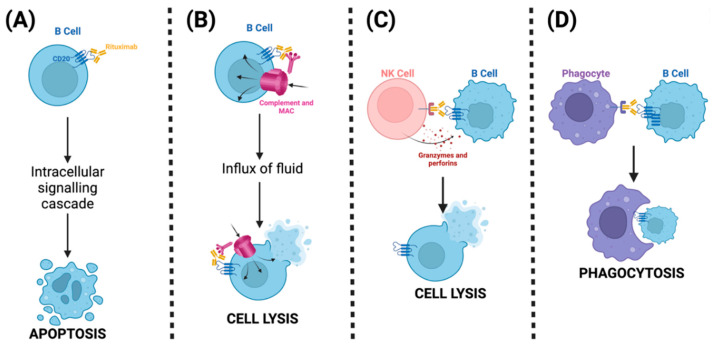
Figure 7.
Mechanism of action of Rituximab, an antibody specific to CD20 on the surface of B cells. (A) Rituximab binds its ligand CD20, which can trigger an intracellular signaling cascade, leading to apoptosis of B cells. (B) Complement activation by rituximab leads to deposition of MACs that cause an influx of fluid and cell lysis of B cells. (C) Fc fragments of rituximab trigger Fc receptors on NK cells, activating them and leading to the release of granzymes and perforins and cell lysis of B cells. (D) Phagocytes are activated through their Fc receptor, recognizing the Fc fragment of rituximab, leading to the degradation of the B cell through phagocytosis. The figure was created with BioRender.com.