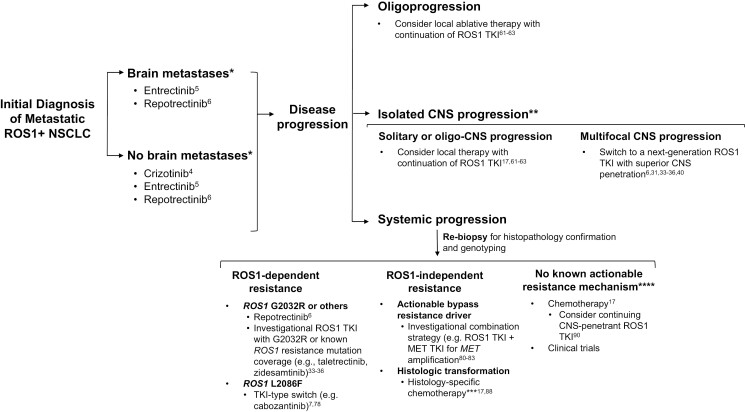
Figure 2.
Approach to treatment of metastatic ROS1 fusion-positive non–small cell lung cancer. Preferred FDA-approved first-line therapy options include crizotinib, entrectinib, or repotrectinib. *Investigational next-generation ROS1 inhibitors taletrectinib and zidesamtinib can also be considered in the first-line setting. At disease progression, the selection of subsequent treatment should be determined based on the pattern of progressive disease and (for addressing systemic progression with switch in systemic therapy) mechanism of drug resistance, if known through rebiopsy. **In addressing CNS progression on a ROS1 inhibitor, multidisciplinary evaluation to assess the optimal use of surgery, radiation, versus switch in systemic therapy is essential. ***Consider continuing ROS1 TKI for nontransformed clones. ****Consider also for polyclonal resistance or concurrent on- and off-target resistance. Abbreviations: TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; ROS1+, ROS1 fusion-positive; CNS, central nervous system.