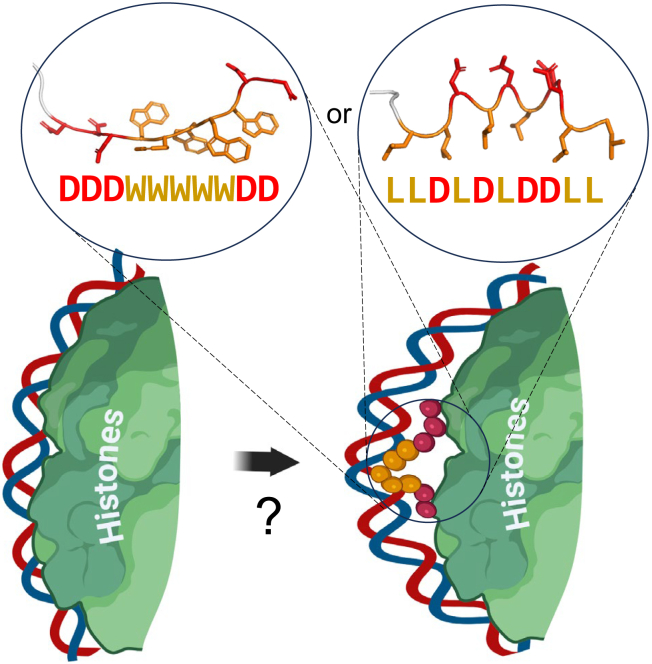
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanism for AD peptide action
On the nucleosome surface the AD peptide (e.g., DDDWWWWWDD or LLDLDLDDLL) interacts with DNA bases via hydrophobic residues (in case of aromatic residues – via intercalation) while interacting with histone tails by electrostatic contacts between acidic residues of the AD peptide and basic residues of histone tails. Created bulge of DNA later is propagated by a chromatin remodeler, similar to the proposed action of DNA groove binders,64 so that the histone octamer is translocated away from the gene promoter opening it for the transcription initiation complex assembly. Note: the structures of depicted peptides are predicted by AlphaFold2 ML model,68 which for the LD peptide suggests that the structure is amphipathic with all Ls situated on one side possibly aligning with the DNA groove. Elements of figure created with BioRender.com.