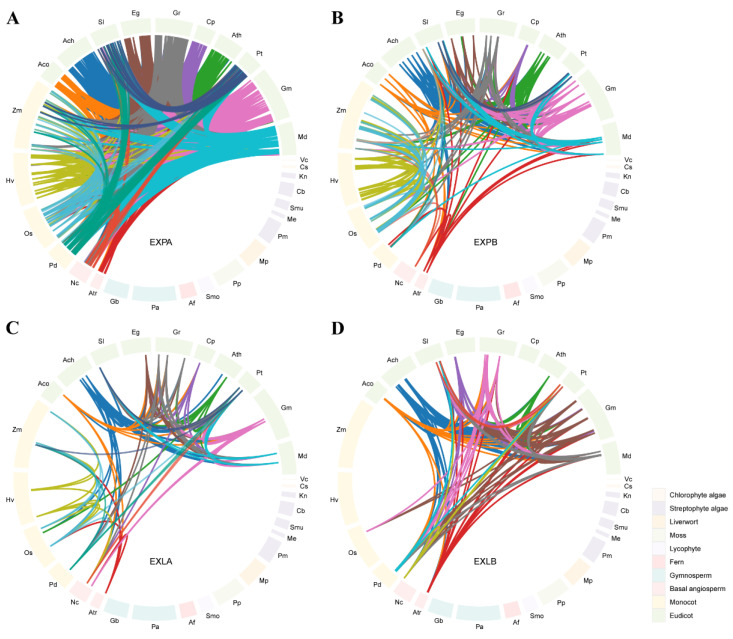
Figure 2.
Schematic representations of the collinear relationships of expansin genes among 29 of the 57 species. (A) EXPA subfamily; (B) EXPB subfamily; (C) EXLA subfamily; (D) EXLB subfamily. The length of each colored bar in the circle indicates the number of expansin genes in a species. Expansin genes within each species are arranged clockwise along a colored bar, according to their genomic coordinates. Each colored line represents a colinear expansin gene pair. The species names are as follows: Volvox carteri (Vc), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea (Cs), Klebsormidium nitens (Kn), Chara braunii (Cb), Spirogloea muscicola (Smu), Mesotaenium endlicherianum (Me), Penium margaritaceum (Pm), Marchantia polymorpha (Mp), Physcomitrium patens (Pp), Selaginella moellendorffii (Smo), Azolla filiculoides (Af), Picea abies (Pa), Ginkgo biloba (Gb), Amborella trichopoda (Atr), Nymphaea colorata (Nc), Phoenix dactylifera (Pd), Oryza sativa (Os), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Zea mays (Zm), Aquilegia coerulea (Aco), Actinidia chinensis (Ach), Solanum lycopersicum (Sl), Eucalyptus grandis (Eg), Gossypium raimondii (Gr), Carica papaya (Cp), Arabidopsis thaliana (Ath), Populus trichocarpa (Pt), Glycine max (Gm), and Malus domestica (Md).