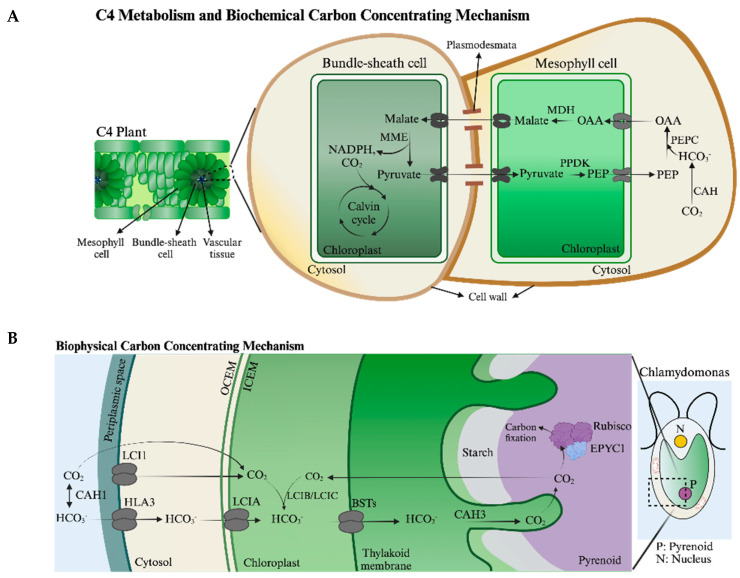
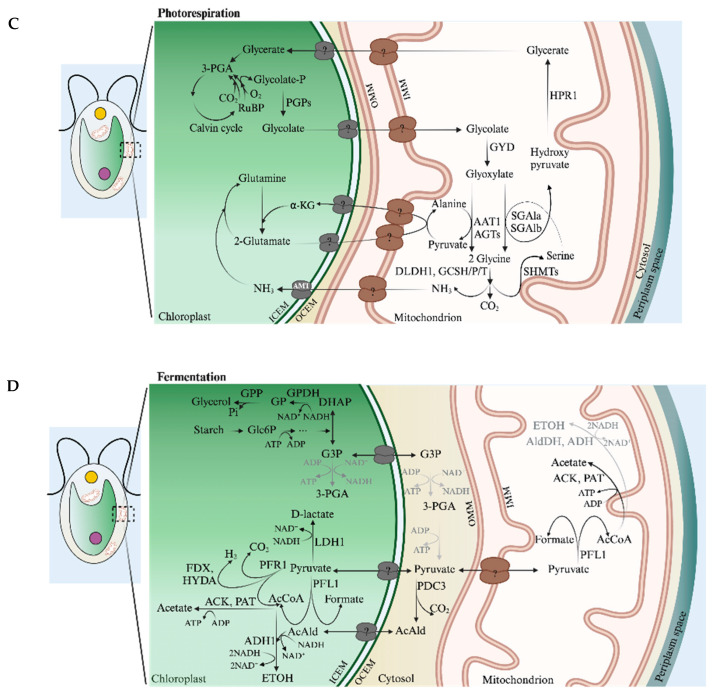
Figure 3.
Metabolite transport required for various metabolic processes in the cell. (A) CO2-concentrating mechanism in a NADP-malic enzyme type C4 plant, such as sugarcane [adapted with some modifications from [156]]. (B) Trafficking of Ci across the plasma membrane and to the pyrenoid. CO2 either directly diffuses across the plasma membrane or is transported by LCI1. It can also be converted to bicarbonate by the activity of CAH1 and transported by HLA3, LCIA, and BSTs through the plasma membrane, chloroplast envelope, and thylakoid membranes, respectively. In the thylakoids that penetrate the pyrenoid, the bicarbonate is converted to CO2 through the activity of CAH3, and then fixed by Rubisco. The components and their locations in the cell are based on studies with Chlamydomonas [157]. (C) Putative metabolite transport required for photorespiration in Chlamydomonas. Transporters responsible for metabolite transport at the chloroplast and mitochondrial envelope membranes; most of these transporters have not yet been identified in Chlamydomonas (except for ammonium transporter, AMT). (D) Fermentation in Chlamydomonas. Glycerol, lactate, CO2, H2, acetate, ethanol, and formate are fermentative end-products. The succinate-producing pathway (reverse TCA cycle) is not shown. Gray arrows in the cytosol indicate omitted steps under fermentative conditions. The ethanol pathway in mitochondria has been shown only at the activity level, so it is indicated in gray. Transporters responsible for metabolite transport at the chloroplast envelope membrane and mitochondria membrane are not yet characterized [adapted from Chlamydomonas Source Book [158]]. AAT1, alanine aminotransferase; ACK, acetate kinase; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; AGT, alanine-glyoxylate transaminase; AldDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; BST, bestrophin; CAH, carbonic anhydrase; DLDH1, dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase; EPYC1, essential pyrenoid component 1; FDX, ferredoxin; GCSH/P/T, glycine cleavage system, H-protein/P-protein/T-protein; GPDH, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GPP, glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase; GYD, glycolate dehydrogenase; HPR, hydroxypyruvate reductase; HYDA, FeFe hydrogenase; LCI, low-CO2 inducible protein; LDH1, lactate dehydrogenase 1; MME, malic enzyme; PDC3, pyruvate decarboxylase; PEPC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; PFL1, pyruvate formate lyase 1; PFR1, pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase; PGP, phosphoglycolate phosphatase; PPDK, pyruvate phosphate dikinase; PAT, phosphate acetyltransferase; Rubisco, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase; SGA1, serine glyoxylate aminotransferase; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; AcAld, acetaldehyde; AcCoA, acetyl coenzyme A; CO2, carbon dioxide; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; ETOH, ethanol; Glc6P, glucose 6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; GP, glycerol-3-phosphate; H2, hydrogen; HCO3−, bicarbonate; NH3, ammonium; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; O2, oxygen; OAA, oxaloacetate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglyceric acid; Pi, inorganic phosphate; RuBP, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. ICEM, inner chloroplast envelope membrane; OCEM, outer chloroplast envelope membrane. Created with BioRender.com.